- accounting transactions are entered as journal entries consisting of the Account name, and either a debit (left side) amount or credit (right side) amount. For each entry the debits and credits must balance, and overall on the trial balance (lists all the debits and credits for all the accounts) must always balance.
- There are 5 main classes of Accounts:
-
Assets: Anything of value that the business owns. This includes tangible assets such as cash, accounts receivable, inventory, buildings, and machinery, as
well as intangible assets such as copyrights, trademarks, and goodwill. Asset accounts normally have a Debit (left side) balance. In transaction entries, a debit to an asset account
shows an increase in its amount, while a credit (right side) indicates a decrease in the asset value.
- Example: Buying Equipment for Cash. One asset (Equipment) increases, and therefore it is Debited. Cash, which is also an asset, is decreased with a Credit.
-
Assets: Anything of value that the business owns. This includes tangible assets such as cash, accounts receivable, inventory, buildings, and machinery, as
well as intangible assets such as copyrights, trademarks, and goodwill. Asset accounts normally have a Debit (left side) balance. In transaction entries, a debit to an asset account
shows an increase in its amount, while a credit (right side) indicates a decrease in the asset value.
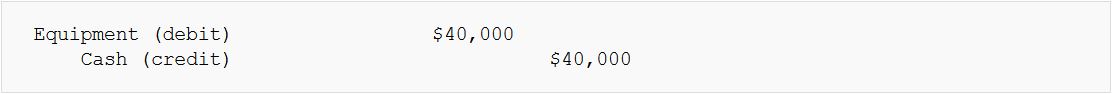
-
Liabilities: Debts and obligations that the business owes. This includes accounts payable, payroll liabilities, and long term debts (such as bonds).
Liabilities accounts normally have a Credit (right side) balance. In transaction entries, a credit to a liability account signifies an increase in its amount, while a debit (left side)
indicates a decrease in the liability value.
- Example: Buying Inventory on credit. Merchandise Inventory (an asset) increases with a debit, and Accounts Payable (a liability) also increases with a credit.
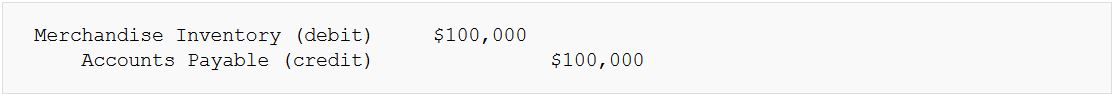
Equity: This is essentially the value that accrues (accumulates) to the owners (shareholders, sole trader…). This ranges from Partner 1’s capital, Partner 1’s profits, retained earnings, etc. Equity accounts normally have a Credit (right side) balance. In transaction entries in the journals, a credit to an equity account signifies an increase in its amount, while a debit (left side) indicates a decrease in the equity value. Always keep the accounting equation in mind:

Since Assets normally have a Debit balance and both liabilities & equity normally have a credit balance, therefore applying the equation above, we always check that the trial balance has a NET value of Zero (the total debits and credits should match).
-
Revenue: This is the entire amount of income made through the sale of goods/services, and is sometimes referred to as Income or Sales. Depending on the nature
of the goods / services being sold, companies track this account either as one big account (e.g. Sales) or as many separate accounts (e.g. Sales Prod 1, Sales Prod 2, Freight Income etc.).
Revenue accounts normally have a Credit (right side) balance, and therefore a credit to a revenue account signifies an increase in its amount, while a debit (left side) indicates a decrease
in the revenue amount. A decrease of revenue would take place in circumstances such as for example sales returns and discounts (explained further down).
- Example: Recording cash sales. Cash is debited because it is an increase in an asset account, and Sales is credited because a Revenue account is increased.
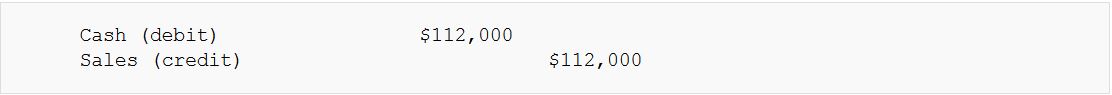
-
Expenses: These are the general costs of doing business. This would include operating expenses such as Salaries Expense, Rent Expense, and Advertising Expense,
as well as non-operating expenses such as Loss on Sale of Assets. Expense accounts normally have a Debit (left side) balance. In transaction entries, a debit to an expense account signifies
an increase in its amount, while a credit indicates a decrease (which rarely occurs, unless an error needs to be corrected).
- Example: The company rents office space at $15,000 per month. Rent Expense is debited, and Cash is credited.
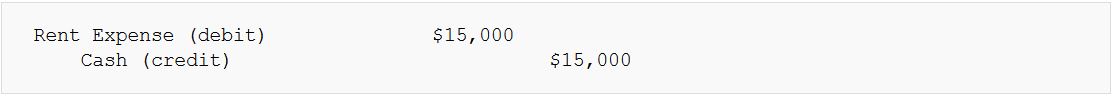
- Some very important aspects to remember in addition to the above:
- Depreciation, Amortization, and Depletion are used to allocate the cost of an asset over its useful life. Depreciation is the allocation over time of tangible assets, Amortization is the allocation over time of intangible assets and Depletion is the allocation over time of natural resources.Accumulated depreciation is a contra-asset account (with a normal Credit balance) used to keep a running total of the depreciation to date. The book value of any asset at any time is the Original Cost less any accumulated depreciation. Contra-asset accounts are listed in the assets section of the balance sheet along with the corresponding asset account, making it easier to see what the assets original cost was and what it is presently valued at. Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts Receivable is also a contra-asset account with a normal credit balance which is netted against the Accounts Receivable account.
- Sales Returns and Allowances & Sales Discounts are contra-revenue accounts, and the normal balance of this account is a Debit. These are used to offset the revenue credit balance.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): This account is used to track how much you paid for goods / material that was held in inventory until it was sold. COGS normally is a debit balance. This account is recorded in entries when a sale is made, and COGS is debited for the cost, while inventory is credited (asset account=>decreased) for the cost.
- Credit Notes/memo/refunds are used to refund customers if they return products bought from the company. The entry for this transaction is usually :

- a summary :

- 6177 reads






