In Washington and several other states, an individual may possess and use marijuana for medicinal purposes with a prescription. 1Federal law prohibits possession and use of marijuana under any circumstances. 2 Technically, this could be a conflict that violates federal supremacy. Until the courts address the federal supremacy issue, however, medical marijuana statutes can continue to stay in effect. Read about a recent ruling regarding the constitutionality of Michigan’s medicinal marijuana law under the Supremacy Clause: http://www.pressandguide.com/articles/2011/04/09/news/doc4d9f557b8ab37805648033.txt.
LAW AND ETHICS : THE ARIZONA IMMIGRATION LAW
Can a State Regulate Immigration?
Arizona passed a comprehensive immigration law designed to seek
out and deport illegal immigrants. This law created a national furor, and its detractors insisted it would lead to unethical racial profiling. The federal government attacked the law in
Federal District Court. 3 Judge Susan Bolton issued a preliminary injunction that stopped enforcement of
the sections of the law that required state law enforcement to check an immigrant’s status while enforcing other laws and that required immigrants to prove they were in the country legally or
risk state charges. 4 Read the District Court’s
preliminary injunction ruling, which is available at this link:
http://graphics8.nytimes.com/packages/pdf/national/20100729_ARIZONA_DOC.pdf
What is the basis for Judge Bolton’s decision? Check your answer using the answer key at the end of the chapter.
Read about the most recent ruling on Arizona’s immigration law by the US Court of Appeals for the Ninth
Circuit: http://latindispatch.com/2011/05/10/
Read about Utah’s immigration law: http://articles.cnn.com/2011-05-%2011/politics/utah.immigration.bill_1_utah-law-gary-herbert-utah-gov?_s=PM:POLITICS
Read about Alabama’s immigration law:http://www.reuters.com/article/2011/06/10/tagblogsfindlawcom2011-freeenterprise-idUS123058502120110610
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Federalism is a system of government in which power is divided between one national, federal government and several independent state governments.
- Congress gets its regulatory authority from Article I § 8 of the federal Constitution. This includes several delegated powers, the commerce clause, and the necessary and
proper clause.
- The commerce clause gives Congress the power to regulate commerce that crosses state lines.
- The necessary and proper clause gives Congress the power to regulate if necessary to carry out all other powers listed in the Constitution.
- The Constitution specifically authorizes Congress to punish piracies and felonies on the high seas, counterfeiting, and treason. Case precedent has also expanded the federal government’s power to enact criminal laws based on the commerce clause and the necessary and proper clause.
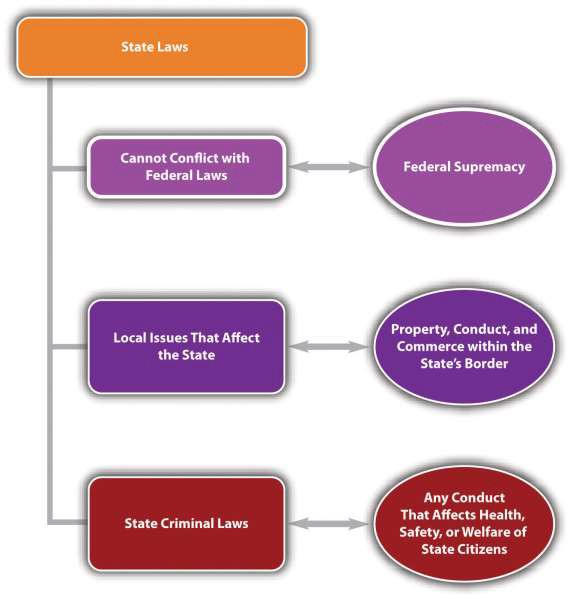
- The federal government is intended to be limited, with the bulk of regulatory authority residing in the states. The federal government is restricted to regulating in the areas designated in Article I § 8 of the federal Constitution. The states can regulate for the health, safety, and welfare of citizens pursuant to their police power, which is set forth in the Tenth Amendment of the federal Constitution.
- Federal criminal laws criminalize conduct that occurs on federal property or involves federal employees, currency, coin, treason, national security, rights secured by the Constitution, or commerce that crosses state lines. State criminal laws make up 90 percent of all criminal laws, are designed to protect state citizens’ health, safety, and welfare, and often criminalize the same conduct as federal criminal laws.
- Federal supremacy, which is set forth in the Supremacy Clause of the federal Constitution, requires courts to follow federal laws if there is a conflict between a federal and state law.
EXERCISES
Answer the following questions. Check your answers using the answer key at the end of the chapter.
- Congress passes a law criminalizing the posting of child pornography on the Internet. Where does Congress get the authority to pass this criminal law? If a state has a criminal law criminalizing the same conduct, can both the state andfederal government prosecute a defendant for one act of downloading child pornography?
- Read U.S. v. Morrison, 529 U.S. 518 (2000). Which part(s) of the Constitution did the US Supreme Court rely on when it held that 42 U.S.C. § 13981 is unconstitutional? The case is available at this link: http://www.law.cornell.edu/supct/html/99-5.ZS.html
- Read Pennsylvaniav. Nelson, 350 U.S. 497 (1956). Why d id the US Supreme Court invalidate the Pennsylvania Sedition Act? The case is available at this link: http://supreme.justia.com/us/350/497/case.html
- 7804 reads






