Available under Creative Commons-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The most common measures are named M0 (narrowest), M1, M2, and M3. In the United States they are defined by the Federal Reserve as follows:
| Measure | Definition |
|---|---|
| M0 | The total of all physical currency, plus accounts at the central bank that can be exchanged for physical currency. |
| M1 | M0 + those portions of M0 held as reserves or vault cash + the amount in demand accounts ("checking" or "current" accounts). |
| M2 | M1 + most savings accounts, money market accounts, and small denomination time deposits (certificates of deposit of under $100,000). |
| M3 | M2 + all other CDs, deposits of eurodollars and repurchase agreements. |
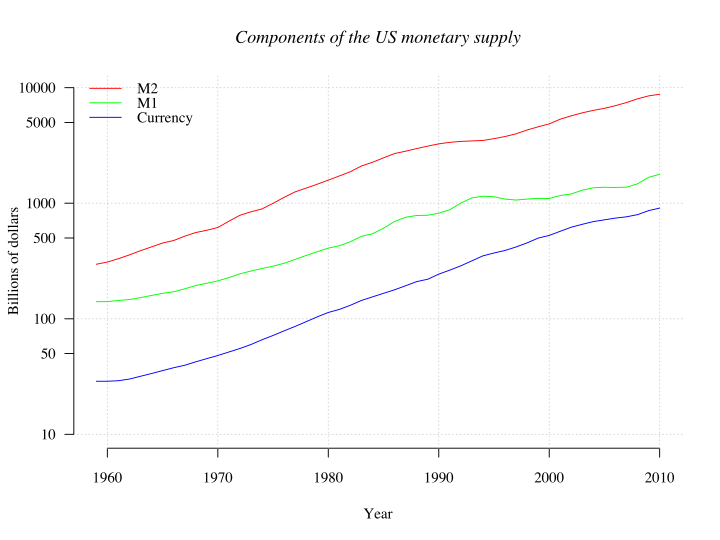
Figure 3.18 Components the U.S. money supply (currency, M1 and M2), 1960–2010
The Federal Reserve stopped publishing M3 statistics in March 2006, saying that the data cost a lot to collect but did not provide significantly useful information 1. The other three money supply measures continue to be provided in detail.
- 1911 reads






