Databases can be organized in many different ways, and thus take many forms. The most popular form of database today is the relational database. Popular examples of relational databases are Microsoft Access, MySQL, and Oracle. A relational database is one in which data is organized into one or more tables. Each table has a set of fields, which define the nature of the data stored in the table. A record is one instance of a set of fields in a table. To visualize this, think of the records as the rows of the table and the fields as the columns of the table. In the example below, we have a table of student information, with each row representing a student and each column representing one piece of information about the student.
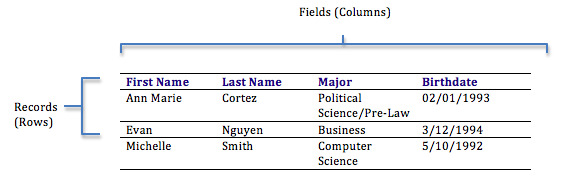
In a relational database, all the tables are related by one or more fields, so that it is possible to connect all the tables in the database through the field(s) they have in common. For each table, one of the fields is identified as a primary key. This key is the unique identifier for each record in the table. To help you understand these terms further, let’s walk through the process of designing a database.
- 1526 reads






