Many times, an organization needs to transmit information over the Internet or transfer it on external media such as a CD or flash drive. In these cases, even with proper authentication and access control, it is possible for an unauthorized person to get access to the data. Encryption is a process of encoding data upon its transmission or storage so that only authorized individuals can read it. This encoding is accomplished by a computer program, which encodes the plain text that needs to be transmitted; then the recipient receives the cipher text and decodes it (decryption). In order for this to work, the sender and receiver need to agree on the method of encoding so that both parties can communicate properly. Both parties share the encryption key, enabling them to encode and decode each other’s messages. This is called symmetric key encryption. This type of encryption is problematic because the key is available in two different places.
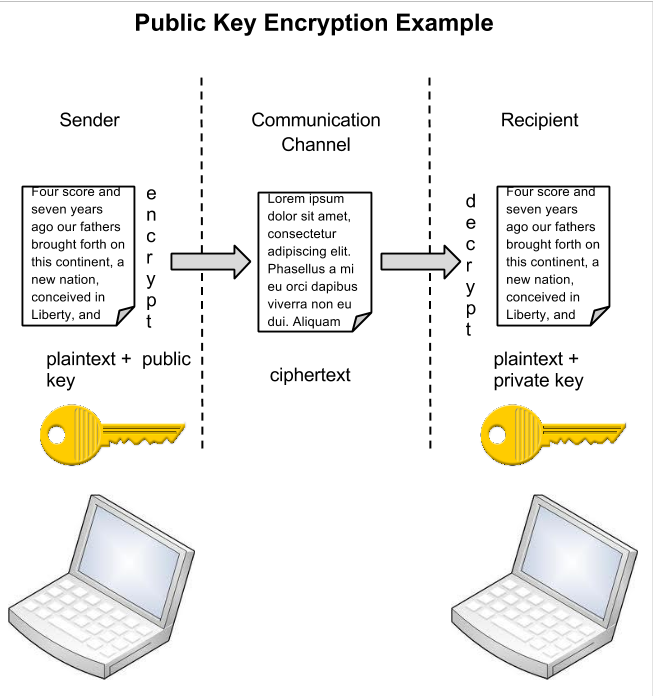
An alternative to symmetric key encryption is public key encryption. In public key encryption, two keys are used: a public key and a private key. To send an encrypted message, you obtain the public key, encode the message, and send it. The recipient then uses the private key to decode it. The public key can be given to anyone who wishes to send the recipient a message. Each user simply needs one private key and one public key in order to secure messages. The private key is necessary in order to decrypt something sent with the public key.
- 1787 reads






