Loops are often used in programs that compute numerical results by starting with an approximate answer and iteratively improving it.
For example, one way of computing square roots is Newton’s method. Suppose that you want to know the square root of a. If you start with almost any estimate, x, you can compute a better estimate with the following formula:
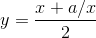
For example, if ais4 and x is 3:
>>> a = 4.0>>> x = 3.0>>> y = (x + a/x) / 2>>> print y2.16666666667
Which is closer to the correct answer ( 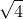 = 2). If we repeat
the process with the new estimate, it gets even closer:
= 2). If we repeat
the process with the new estimate, it gets even closer:
>>> x = y>>> y = (x + a/x) / 2>>> print y2.00641025641
After a few more updates, the estimate is almost exact:
>>> x = y>>> y = (x + a/x) / 2>>> print y2.00001024003>>> x = y>>> y = (x + a/x) / 2>>> print y2.00000000003
In general we don’t know ahead of time how many steps it takes to get to the right answer, but we know when we get there because the estimate stops changing:
>>> x = y>>> y = (x + a/x) / 2>>> print y2.0>>> x = y>>> y = (x + a/x) / 2>>> print y2.0
When y == x, we can stop. Here is a loop that starts with an initial estimate, x, and improves it until it stops changing:
while True:
print x
y = (x + a/x) / 2
if y == x:
break
x = y
For most values of a this works fine, but in general it is dangerous to test float equality. Floating-point values are only approximately right: most rational
numbers, like 1/3, and irrational numbers, like 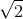 , can’t be
represented exactly with a float.
, can’t be
represented exactly with a float.
Rather than checking whether x and y are exactly equal, it is safer to use the built-in func tion abs to compute the absolute value, or magnitude, of the difference between them:
if abs(y-x) < epsilon:
break
Where epsilon has a value like 0.0000001 that determines how close is close enough.
Exercise 7.2.Encapsulate this loop in a function called square_rootthat takes a as a parameter, chooses a reasonable value of x, and returns an estimate of the square root of a.
- 3187 reads






