The standard normal distribution is a normal distribution of standardized values called z-scores. A z-score is measured in units of the standard deviation. For example, if the mean of a normal distribution is 5 and the standard deviation is 2, the value 11 is 3 standard deviations above (or to the right of) the mean. The calculation is:
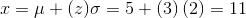
The z-score is 3.
The mean for the standard normal distribution is 0 and the standard deviation is 1. The transformation 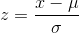 produces the distribution Z∼ N (0, 1) . The value x comes from a normal distribution with mean µ and standard deviation σ.
produces the distribution Z∼ N (0, 1) . The value x comes from a normal distribution with mean µ and standard deviation σ.
- 2200 reads






