Available under Creative Commons-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/733d1554-5d75-4798-9e54-7dcdc1ee5690@5.40
The arrow in the graph below points to the area to the left of x. This area is represented by the probability P (X<x). Normal tables, computers, and calculators provide or calculate the probability P (X<x).
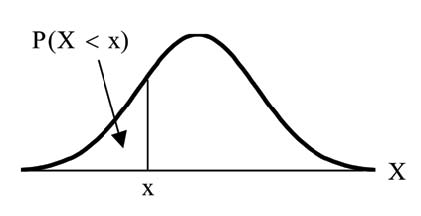
The area to the right is then P (X>x) = 1 − P (X<x).
Remember, P (X<x)= Area to the left of the vertical line through x.
P (X>x) = 1 − P (X<x) = Area to the right of the vertical line through x.
P (X<x) is the same as P (X ≤ x) and P (X>x) is the same as P (X ≥ x) for continuous distributions.
- 2978 reads






