When executives choose strategies, an organization’s resources and capabilities should be examined alongside consideration of its value chain. A value chain charts the path by which products and services are created and eventually sold to customers. 1 The term value chain reflects the fact that, as each step of this path is completed, the product becomes more valuable than it was at the previous step (Figure 4.11 Adding Value within a Value Chain ). Within the lumber business, for example, value is added when a tree is transformed into usable wooden boards; the boards created from a tree can be sold for more money than the price of the tree.
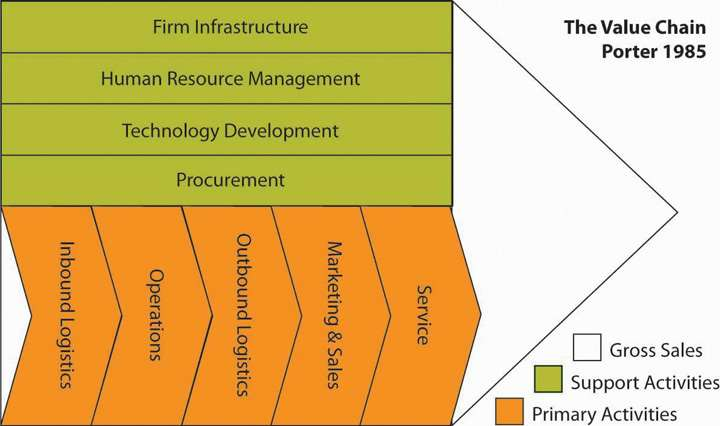
Value chains include both primary and secondary activities. Primary activities are actions that are directly involved in creating and distributing goods and services. Consider a simple illustrative example: doughnut shops. Doughnut shops transform basic commodity products such as flour, sugar, butter, and grease into delectable treats. Value is added through this process because consumers are willing to pay much more for doughnuts than they would be willing to pay for the underlying ingredients.
There are five primary activities. Inbound logistics refers to the arrival of raw materials. Although doughnuts are seen by most consumers as notoriously unhealthy, the Doughnut Plant in New York City has carved out a unique niche for itself by obtaining organic ingredients from a local farmer’s market. Operations refers to the actual production process, while outbound logistics tracks the movement of a finished product to customers. One of Southwest Airlines’ unique capabilities is moving passengers more quickly than its rivals. This advantage in operations is based in part on Southwest’s reliance on one type of airplane (which speeds maintenance) and its avoidance of advance seat assignments (which accelerates the passenger boarding process).
Attracting potential customers and convincing them to make purchases is the domain of marketing and sales. For example, people cannot help but notice Randy’s Donuts in Inglewood, California, because the building has a giant doughnut on top of it. Finally, service refers to the extent to which a firm provides assistance to their customers. Voodoo Donuts in Portland, Oregon, has developed a clever website (voodoodoughnut.com) that helps customers understand their uniquely named products, such as the Voodoo Doll, the Texas Challenge, the Memphis Mafia, and the Dirty Snowball.
Secondary activities are not directly involved in the evolution of a product but instead provide important underlying support for primary activities. Firm infrastructure refers to how the firm is organized and led by executives. The effects of this organizing and leadership can be profound. For example, Ron Joyce’s leadership of Canadian doughnut shop chain Tim Hortons was so successful that Canadians consume more doughnuts per person than all other countries. In terms of resource-based theory, Joyce’s leadership was clearly a valuable and rare resource that helped his firm prosper.
Also important is human resource management, which involves the recruitment, training, and compensation of employees. A recent research study used data from more than twelve thousand organizations to demonstrate that the knowledge, skills, and abilities of a firm’s employees can act as a strategic resource and strongly influence the firm’s performance.2Certainly, the unique level of dedication demonstrated by employees at Southwest Airlines has contributed to that firm’s excellent performance over several decades.
Technology refers to the use of computerization and telecommunications to support primary activities. Although doughnut making is not a high-tech business, technology plays a variety of roles for doughnut shops, such as allowing customers to use credit cards. Procurement is the process of negotiating for and purchasing raw materials. Large doughnut chains such as Dunkin’ Donuts and Krispy Kreme can gain cost advantages over their smaller rivals by purchasing flour, sugar, and other ingredients in bulk. Meanwhile, Southwest Airlines has gained an advantage over its rivals by using futures contracts within its procurement process to minimize the effects of rising fuel prices.
- 12279 reads






