Adrienne Watt
Even the most carefully planned project can run into trouble. No matter how well you plan, your project can always encounter unexpected problems. Team members get sick or quit, resources that you were depending on turn out to be unavailable, even the weather can throw you for a loop (e.g., a snowstorm). So does that mean that you’re helpless against unknown problems? No! You can use risk planning to identify potential problems that could cause trouble for your project, analyze how likely they are to occur, take action to prevent the risks you can avoid, and minimize the ones that you can’t.
A risk is any uncertain event or condition that might affect your project. Not all risks are negative. Some events (like finding an easier way to do an activity) or conditions (like lower prices for certain materials) can help your project. When this happens, we call it an opportunity; but it’s still handled just like a risk.
There are no guarantees on any project. Even the simplest activity can turn into unexpected problems. Anything that might occur to change the outcome of a project activity, we call that a risk. A risk can be an event (like a snowstorm) or it can be a condition (like an important part being unavailable). Either way, it’s something that may or may not happen …but if it does, then it will force you to change the way you and your team work on the project.
If your project requires that you stand on the edge of a cliff, then there’s a risk that you could fall. If it’s very windy out or if the ground is slippery and uneven, then falling is more likely (Figure 16.1 Risk Management Options ).
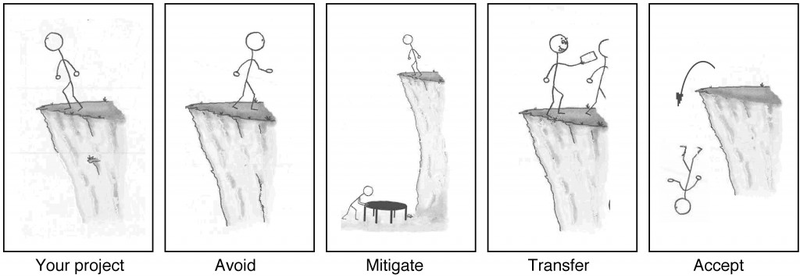
When you’re planning your project, risks are still uncertain: they haven’t happened yet. But eventually, some of the risks that you plan for do happen, and that’s when you have to deal with them. There are four basic ways to handle a risk.
- Avoid: The best thing you can do with a risk is avoid it. If you can prevent it from happening, it definitely won’t hurt your project. The easiest way to avoid this risk is to walk away from the cliff, but that may not be an option on this project.
- Mitigate: If you can’t avoid the risk, you can mitigate it. This means taking some sort of action that will cause it to do as little damage to your project as possible.
- Transfer: One effective way to deal with a risk is to pay someone else to accept it for you. The most common way to do this is to buy insurance.
- Accept: When you can’t avoid, mitigate, or transfer a risk, then you have to accept it. But even when you accept a risk, at least you’ve looked at the alternatives and you know what will happen if it occurs. If you can’t avoid the risk, and there’s nothing you can do to reduce its impact, then accepting it is your only choice.
By the time a risk actually occurs on your project, it’s too late to do anything about it. That’s why you need to plan for risks from the beginning and keep coming back to do more planning throughout the project.
The risk management plan tells you how you’re going to handle risk in your project. It documents how you’ll assess risk, who is responsible for doing it, and how often you’ll do risk planning (since you’ll have to meet about risk planning with your team throughout the project).
Some risks are technical, like a component that might turn out to be difficult to use. Others are external, like changes in the market or even problems with the weather.
It’s important to come up with guidelines to help you figure out how big a risk’s potential impact could be. The impact tells you how much damage the risk would cause to your project. Many projects classify impact on a scale from minimal to severe, or from very low to very high. Your risk management plan should give you a scale to help figure out the probability of the risk. Some risks are very likely; others aren’t.
- 3009 reads






