Word processing software programs display a document on a computer’s screen and allow the user to enter and edit text. When the file is saved to a storage device, the text and all the various formatting such as font and font size are converted to a code for efficient storage. The code varies from one word processing program to another and even between releases of the same program.
The most common word processing program, by a wide margin, is Microsoft Word (MS Word). Several releases of MS Word run on the Windows operating system and on the Macintosh operating system. Versions of MS Word released prior to 2007 save files in a proprietary format. The format is indicated by a period and a three-letter extension—.doc—that is automatically attached to the file when it is saved. Beginning with MS Word 2007 for Windows and MS Word 2008 for Macintosh, files are saved using a different format that is indicated by a period and a four-letter extension—.docx—that identify the newer format.
Almost all word processing programs have the ability to save files in the .doc file format, and it is a common standard for word processing files. Newer versions of word processing programs, including MS Word 2007 and MS Word for Mac 2008, can save files in the older .doc format. There are new features in MS Word 2007—such as the ability to format citations in a variety of styles, including APA, MLA, and Chicago—that are lost when the file is saved in the .doc format. Older versions of MS Word can be adapted to read the newer .docx file formats by downloading and installing a compatibility program that is available at no cost from Microsoft’s Web site. Display of document file extensions is hidden by default in the Windows operating system. They can be displayed by turning off this feature. Instructions for displaying the file extensions are available from the operating system’s help menu. In the Windows Vista operating system, the option is found on the Control Panel, in Appearance and Personalization, in Folder Options, on the View tab, under Advanced Settings, as shown in Figure 6.8.
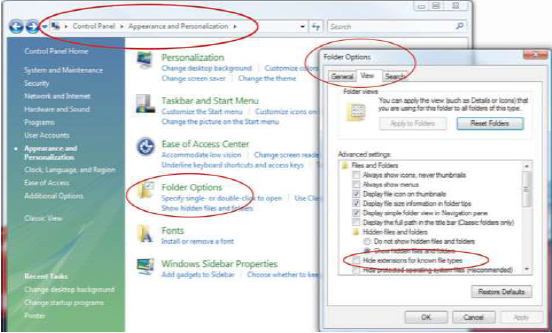
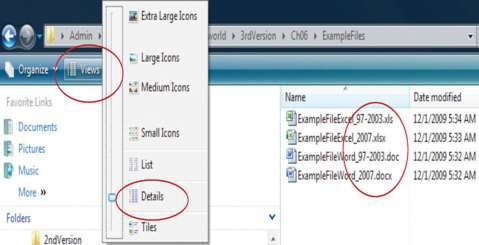
When a list of files is displayed in a dialog box, choose the Details option. In Windows Vista, the Details option is on the View button, as shown in Figure 6.9.
- 2129 reads






