The evaluation of expressions is accomplished with arithmetic operators as we use them in scientific calculators. Note the addtional operators shown in the table below:
|
Operator |
Name |
Description |
|
+ |
Plus |
Addition |
|
- |
Minus |
Subtraction |
|
* |
Asterisk |
Multiplication |
|
/ |
Forward Slash |
Division |
|
\ |
Back Slash |
Left Matrix Division |
|
^ |
Caret |
Power |
|
.* |
Dot Asterisk |
Array multiplication (element-wise) |
|
./ |
Dot Slash |
Right array divide (element-wise) |
|
.\ |
Dot Back Slash |
Left array divide (element-wise) |
|
.^ |
Dot Caret |
Array power (element-wise) |
NOTE: The backslash operator is used to solve linear systems of equations, see Linear Equations .
IMPORTANT: Matrix is a rectangular array of numbers and formed by rows and columns.
For example 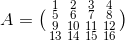 . In this example A consists of 4 rows and 4 columns and therefore is a 4x4 matrix.
(see Wikipedia 1).
. In this example A consists of 4 rows and 4 columns and therefore is a 4x4 matrix.
(see Wikipedia 1).
IMPORTANT: Row vector is a special matrix that contains only one row. In other words, a row vector is a 1xn matrix where n is the number of elements in the row vector. 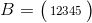
IMPORTANT: Column vector is also a special matrix. As the term implies, it contains only one column. A column vector is an nx1 matrix where n is the number of elements in the column vector.
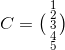
NOTE: Array operations refer to element-wise calculations on the arrays, for example if x is an a by b matrix and y is a c by d matrix then x.*y can be performed only if a=c and b=d. Consider
the following example, x consists of 2 rows and 3 columns and therefore it is a 2x3 matrix. Likewise, y has 2 rows and 3 columns and an array operation is possible.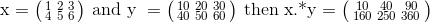
- 1952 reads






