The Internet Protocol (IP) is the network layer protocol of the TCP/IP protocol suite. IP allows the applications running above the transport layer (UDP/TCP) to use a wide range of heterogeneous datalink layers. IP was designed when most point-to-point links were telephone lines with modems. Since then, IP has been able to use Local Area Networks (Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI, ...), new wide area data link layer technologies (X.25, ATM, Frame Relay, ...) and more recently wireless networks (802.11, 802.15, UMTS, GPRS, ...). The flexibility of IP and its ability to use various types of underlying data link layer technologies is one of its key advantages.
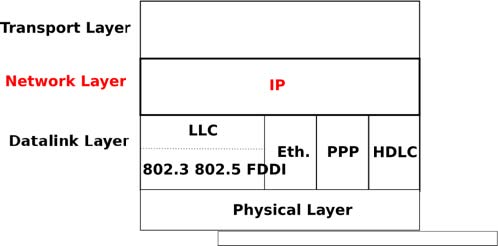
The current version of IP is version 4 specified in RFC 791. We first describe this version and later explain IP version 6, which is expected to replace IP version 4 in the not so distant future.
- 1980 reads






