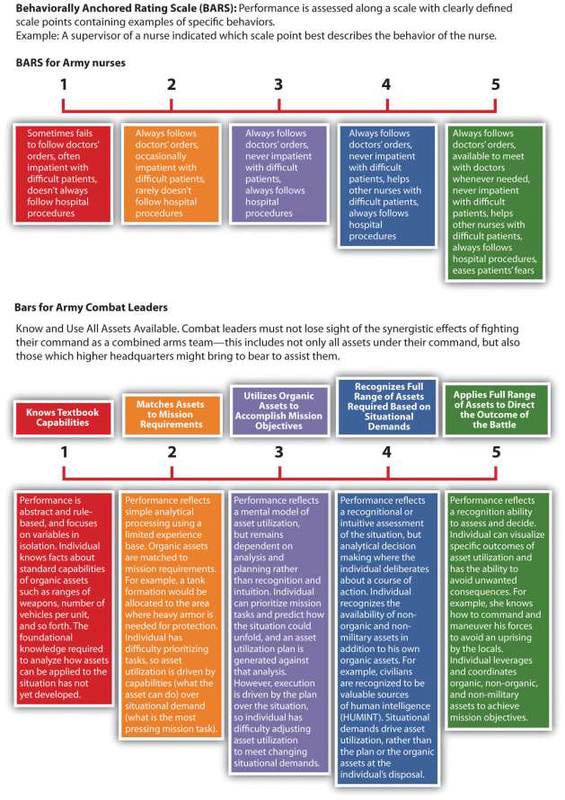
A BARS method first determines the main performance dimensions of the job, for example, interpersonal relationships. Then the tool utilizes narrative information, such as from a critical incidents file, and assigns quantified ranks to each expected behavior. In this system, there is a specific narrative outlining what exemplifies a “good” and “poor” behavior for each category. The advantage of this type of system is that it focuses on the desired behaviors that are important to complete a task or perform a specific job. This method combines a graphic rating scale with a critical incidents system. The US Army Research Institute 1 developed a BARS scale to measure the abilities of tactical thinking skills for combat leaders. Figure 11.4 provides an example of how the Army measures these skills.
How Would You Handle This?
Playing Favorites
You were just promoted to manager of a high-end retail store. As you are sorting through your responsibilities, you receive an e-mail from HR outlining the process for performance evaluations. You are also notified that you must give two performance evaluations within the next two weeks. This concerns you, because you don’t know any of the employees and their abilities yet. You aren’t sure if you should base their performance on what you see in a short time period or if you should ask other employees for their thoughts on their peers’ performance. As you go through the files on the computer, you find a critical incident file left from the previous manager, and you think this might help. As you look through it, it is obvious the past manager had “favorite” employees and you aren’t sure if you should base the evaluations on this information. How would you handle this?
How Would You Handle This?
https://api.wistia.com/v1/medias/1360849/embed
The author discusses the How Would You Handle This situation in this chapter at:https://api.wistia.com/v1/medias/1360849/embed.
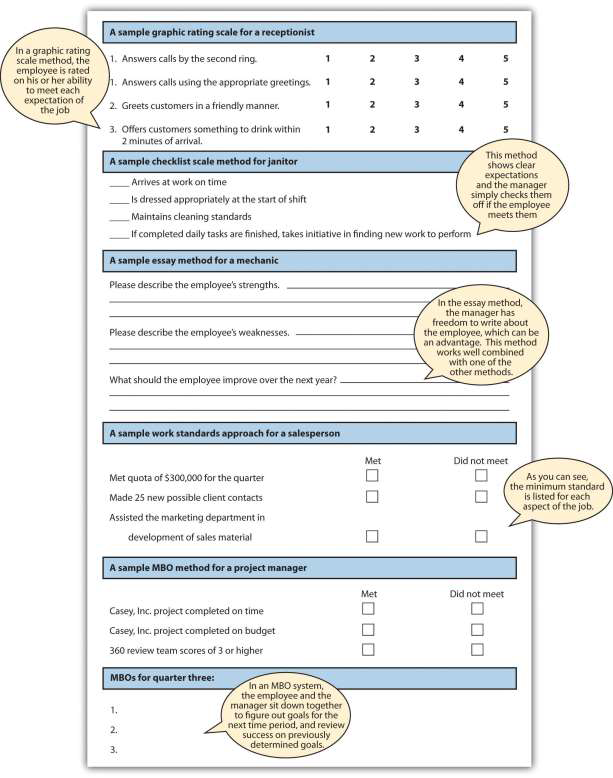
| Type of Performance Appraisal Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Graphic Rating Scale | Inexpensive to develop | Subjectivity |
| Easily understood by employees and managers | Can be difficult to use in making compensation and promotion decisions | |
| Essay | Can easily provide feedback on the positive abilities of the employee | Subjectivity |
| Writing ability of reviewer impacts validity | ||
| Time consuming (if not combined with other methods) | ||
| Checklist scale | Measurable traits can point out specific behavioral expectations | Does not allow for detailed answers or explanations (unless combined with another method) |
| Critical Incidents | Provides specific examples | Tendency to report negative incidents |
| Time consuming for manager | ||
| Work Standards Approach | Ability to measure specific components of the job | Does not allow for deviations |
| Ranking | Can create a high-performance work culture | Possible bias |
| Validity depends on the amount of interaction between employees and manager | ||
| Can negatively affect teamwork | ||
| MBOs | Open communication | Many only work for some types of job titles |
| Employee may have more “buy-in” | ||
| BARS | Focus is on desired behaviors | Time consuming to set up |
| Scale is for each specific job | ||
| Desired behaviors are clearly outlined | ||
| No one performance appraisal is best, so most companies use a variety of methods to ensure the best results. | ||
Key Takeaways
- When developing performance appraisal criteria, it is important to remember the criteria should be job specific and industry specific.
- The performance appraisal criteria should be based on the job specifications of each specific job. General performance criteria are not an effective way to evaluate an employee.
- The rating is the scale that will be used to evaluate each criteria item. There are a number of different rating methods, including scales of 1–5, yes or no questions, and essay.
- In a graphic rating performance evaluation, employees are rated on certain desirable attributes. A variety of rating scales can be used with this method. The disadvantage is possible subjectivity.
- An essay performance evaluation will ask the manager to provide commentary on specific aspects of the employee’s job performance.
- A checklist utilizes a yes or no rating selection, and the criteria are focused on components of the employee’s job.
- Some managers keep a critical incidents file. These incidents serve as specific examples to be written about in a performance appraisal. The downside is the tendency to record only negative incidents and the time it can take to record this.
- The work standards performance appraisal approach looks at minimum standards of productivity and rates the employee performance based on minimum expectations. This method is often used for sales forces or manufacturing settings where productivity is an important aspect.
- In a ranking performance evaluation system, the manager ranks each employee from most valuable to least valuable. This can create morale issues within the workplace.
- An MBO or management by objectives system is where the manager and employee sit down together, determine objectives, then after a period of time, the manager assesses whether those objectives have been met. This can create great development opportunities for the employee and a good working relationship between the employee and manager.
- An MBO’s objectives should be SMART: specific, measurable, attainable, results oriented, and time limited.
- A BARS approach uses a rating scale but provides specific narratives on what constitutes good or poor performance.
Exercise
- Review each of the appraisal methods and discuss which one you might use for the following types of jobs, and discuss your choices.
- Administrative Assistant
- Chief Executive Officer
- Human Resource Manager
- Retail Store Assistant Manager
- 61695 reads






