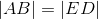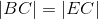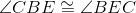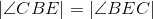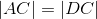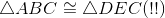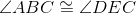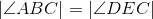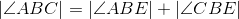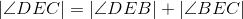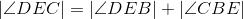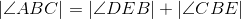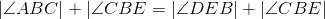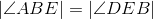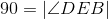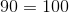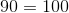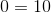Construct a four-sided figure ABED as follows:
- |∠ABE| = 90 ◦
- |∠DEB| = 100 ◦
- |AB| = |ED|
Using that as a starting point, we now tinker a bit to show that 90 = 100:
- Draw the perpendicular bisectors to BE and AD; call the point where they meet "C".
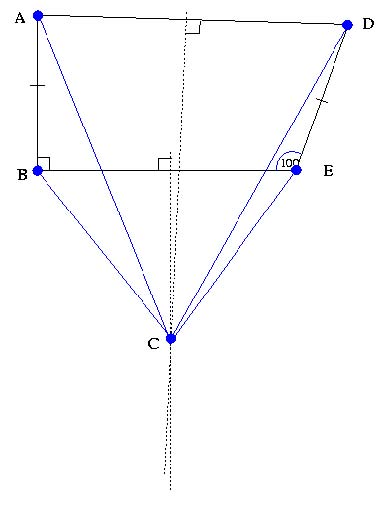
Looking at this figure, some warning flags should be going up: How do we know C lies below BD? Might it lie above BD? Or exactly on BD? It turns out that the argument below is the same in all of these cases, though you'll certainly want to verify this to yourself later.
|
1 |
|
By construction. |
|
2 |
|
C is on the perpendicular bisector of BE (thus ,BEC is isosceles). |
|
3 |
|
Base angles of isosceles triangle BEC are congruent. |
|
4 |
|
Congruent angles have equal measures; line 3. |
|
5 |
|
C is on the perpendicular bisector of AD (thus ,ADC is isosceles). |
|
6 |
|
Triangles with three congruent sides are congruent (Euclid's Side-Side-Side congruence theorem); lines 1,2,5. |
|
7 |
(From here, it's just routine steps to conclude 90 = 100:) |
|
|
8 |
|
Corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent; line 6. |
|
9 |
|
Congruent angles have equal measures; line 8. |
|
10 |
|
By construction. |
|
11 |
|
By construction. |
|
12 |
|
Substituting equals with equals; lines 11 and 4. |
|
13 |
|
Substituting equals with equals; lines 12 and 9. |
|
14 |
|
Substituting equals with equals; lines 13 and 10. |
|
15 |
|
Subtracting equals from equals remains equal. |
|
16 |
|
By construction, and substituting equals with equals; line 15. |
|
17 |
|
By construction, and substituting equals with equals; line 16. |
|
1 |
|
Previous theorem. |
|
2 |
|
Subtracting equals (90) from equals remains equal. |
|
3 |
|
Dividing equals by non-zero equals (10) remains equal. |
Exercise 1.1.1
If you feel this result is incorrect, then the challenge for you is to find the first line which is false. You may have noticed that the proof given here has some very minuscule steps e.g. "Congruent angles have equal measure." Usually such simple steps can be omitted, since they are obvious to any reader. We include them for a few reasons:
- As a careful thinker, you should recognize that such small steps really are part of the complete reasoning, even if they're not worth mentioning continually.
- If a computer is checking a proof, it needs to actually include those steps.
- Programmers do need to be concerned with distinctions about (abstract) types the difference between angles and their measures, in this case.
- Sometimes a line's justification is glibly given as "by construction", when that may not even be correct !-).
In this course, we'll spend a few weeks working with proofs which do include all the small, pedantic steps, to instill a mental framework for what a rigorous proof is. But after that, you can relax your proofs to leave out such low-level steps, once you appreciate that they are being omitted.
- 4227 reads