An effective price floor sets the price above the market-clearing price. A minimum wage is the most widespread example in the Canadian economy. Provinces each set their own minimum, and it is
seen as a way of protecting the well-being of low-skill workers. Such a floor is illustrated in Figure 3.7. The free-market equilibrium is again Eo, but the effective market outcome is the combination of price and quantity
corresponding to the point 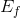 at the price floor,
at the price floor, 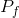 . In this instance, there is excess supply equal to the amount
. In this instance, there is excess supply equal to the amount 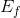 C.
C.
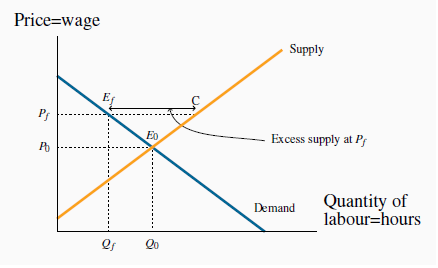
In a free market the equilibrium is Eo. A minimum wage of 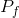 raises the hourly wage, but reduces the hours demanded to
raises the hourly wage, but reduces the hours demanded to 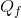 .
Thus
.
Thus 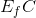 is the excess supply.
is the excess supply.
Note that there is a similarity between the outcomes defined in the floor and ceiling cases: The quantity actually traded is the lesser of the supply quantity and demand quantity at the going price: the short side dominates.
- 瀏覽次數:2826






