You can think of a sampling distribution as a relative frequency distribution with a great many samples. (See Sampling and Data for a review of relative frequency). Suppose thirty randomly selected students were asked the number of movies they watched the previous week. The results are in the relative frequency table shown below.
|
# of movies |
Relative Frequency |
|---|---|
|
0 |
5/30 |
|
1 |
15/30 |
|
2 |
6/30 |
|
3 |
4/30 |
|
4 |
1/30 |
If you let the number of samples get very large (say, 300 million or more), the relative frequency table becomes a relative frequency distribution.
A statistic is a number calculated from a sample. Statistic examples include the mean, the median and the mode as well as others. The sample mean 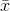 is an example of a statistic which estimates the population mean µ.
is an example of a statistic which estimates the population mean µ.
- 2275 reads






