It is interesting to note that each of the social influences on our sense of self that we have discussed can be harnessed as a way of protecting our self-esteem. The final influence we will explore can also be used strategically to elevate not only our own esteem, but the esteem we have in the eyes of others. Positive self-esteem occurs not only when we do well in our own eyes but also when we feel that we are positively perceived by the other people we care about.

Because it is so important to be seen as competent and productive members of society, people naturally attempt to present themselves to others in a positive light. We attempt to convince others that we are good and worthy people by appearing attractive, strong, intelligent, and likable and by saying positive things to others (Jones & Pittman, 1982; Schlenker, 2003). The tendency to present a positive self-image to others, with the goal of increasing our social status, is known as self-presentation, and it is a basic and natural part of everyday life.
A big question in relation to self-presentation is the extent to which it is an honest versus more strategic, potentially dishonest enterprise. The sociologist Erving Goffman (1959) developed an influential theory of self-presentation and described it as a mainly honest process, where people need to present the parts of themselves required by the social role that they are playing in a given situation. If everyone plays their part according to accepted social scripts and conventions, then the social situation will run smoothly and the participants will avoid embarrassment. Seen in this way, self-presentation is a transparent process, where we are trying to play the part required of us, and we trust that others are doing the same. Other theorists, though, have viewed self-presentation as a more strategic endeavor, which may involve not always portraying ourselves in genuine ways (e.g., Jones & Pittman, 1982). As is often the case with two seemingly opposing perspectives, it is quite likely that both are true in certain situations, depending on the social goals of the actors.
Different self-presentation strategies may be used to create different emotions in other people, and the use of these strategies may be evolutionarily selected because they are successful (Toma, Hancock, & Ellison, 2008). Edward Jones and Thane Pittman (1982) described five self-presentation strategies, each of which is expected to create a resulting emotion in the other person:
- The goal of ingratiation is to create liking by using flattery or charm.
- The goal of intimidation is to create fear by showing that you can be aggressive.
- The goal of exemplification is to create guilt by showing that you are a better person than the other.
- The goal of supplication is to create pity by indicating to others that you are helpless and needy.
- The goal of self-promotion is to create respect by persuading others that you are competent.

No matter who is using it, self-presentation can easily be overdone, and when it is, it backfires. People who overuse the ingratiation technique and who are seen as obviously and strategically trying to get others to like them are often disliked because of this. Have you ever had a slick salesperson obviously try to ingratiate him- or herself with you just so you will buy a particular product, and you end up not liking the person and making a hasty retreat from the premises? People who overuse the exemplification or self-promotion strategies by boasting or bragging, particularly if that boasting does not appear to reflect their true characteristics, may end up being perceived as arrogant and even self-deluded (Wosinska, Dabul, Whetstone-Dion, & Cialdini, 1996). Using intimidation can also often backfire; acting more modestly may be more effective. Again, the point is clear: we may want to self-promote with the goal of getting others to like us, but we must also be careful to consider the point of view of the other person. Being aware of these strategies is not only useful for better understanding how to use them responsibly ourselves, it can also help us to understand that other people’s behaviors may often reflect their self-presentational concerns. This can, in turn, facilitate better empathy for others, particularly when they are exhibiting challenging behaviors (Friedlander & Schwartz, 1985). For instance, perhaps someone’s verbally aggressive behavior toward you is more about that person being afraid rather than about his or her desire to do you harm.
Now that we have explored some of the commonly used self-presentation tactics, let’s look at how they manifest in specific social behaviors. One concrete way to self-promote is to display our positive physical characteristics. A reason that many of us spend money on improving our physical appearance is the desire to look good to others so that they will like us. We can also earn status by collecting expensive possessions such as fancy cars and big houses and by trying to associate with high-status others. Additionally, we may attempt to dominate or intimidate others in social interactions. People who talk more and louder and those who initiate more social interactions are afforded higher status. A businessman who greets others with a strong handshake and a smile, and people who speak out strongly for their opinions in group discussions may be attempting to do so as well. In some cases, people may even resort to aggressive behavior, such as bullying, in attempts to improve their status (Baumeister, Smart, & Boden, 1996).
Self-promotion can also be pursued in our online social behaviors. For example, a study in Taiwan conducted by Wang and Stefanone (2013) used survey methodology to investigate the relationship between personality traits, self-presentation and the use of check-ins on Facebook. Interestingly, narcissism was found to predict scores on a measure of exhibitionistic, self-promoting use of Facebook check-ins, which included items like “I check in so people know that I am with friends,” and “I expect friends to like or leave comments on my check-in status on Facebook.”
Other studies have also found associations between narcissistic traits and self-promotional activity on Facebook. Mehdizadeh (2010), for example, found that narcissistic personality scores were positively correlated with the amount of daily logins on Facebook and the duration of each login. Furthermore, narcissistic traits were related to increased use of self-promotional material in the main photo, view photos, status updates, and notes sections of people’s Facebook pages.
Analysis of the content and language used in Facebook postings has also revealed that they are sometimes used by individuals to self-promote. Bazarova, Taft, Choi, and Cosley (2013) explored self-presentation through language styles used in status updates, wall posts, and private messages from 79 participants. The use of positive emotion words was correlated with self-reported self-presentation concern in status updates. This is consistent with the idea that people share positive experiences with Facebook friends partly as a self-enhancement strategy.
Online self-presentation doesn’t seem to be limited to Facebook usage. There is also evidence that self-promotional concerns are often a part of blogging behaviors, too. Mazur and Kozarian (2010), for example, analyzed the content of adolescents’ blog entries and concluded that a careful concern for self-presentation was more central to their blogging behavior than direct interaction with others. This often seems to apply to micro-blogging sites like Twitter. Marwick and Boyd (2011) found that self-presentational strategies were a consistent part of celebrity tweeting, often deployed by celebrities to maintain their popularity and image.
You might not be surprised to hear that men and women use different approaches to self-presentation. Men are more likely to present themselves in an assertive way, by speaking and interrupting others, by visually focusing on the other person when they are speaking, and by leaning their bodies into the conversation. Women, on the other hand, are more likely to be modest; they tend to create status by laughing and smiling, and by reacting more positively to the statements of others (Dovidio, Brown, Heltman, Ellyson, & Keation, 1988).
These gender differences are probably in large part socially determined as a result of the different reinforcements that men and women receive for using particular self-presentational strategies. For example, self-promoting by speaking out and acting assertively can be more effective for men than it is for women, in part because cross-culturally consistent stereotypes tend to depict assertiveness as more desirable in men than in women. These stereotypes can have very important consequences in the real world. For instance, one of the reasons for the “glass ceiling” existing in some occupations (where women experience discrimination in reaching top positions in organizations) may be attributable to the more negative reactions that their assertive behaviors, necessary for career advancement, receive than those of their male colleagues (Eagly & Carli, 2007).
There are also some cultural differences in the extent to which people use self-presentation strategies in social contexts. For instance, when considering job interviews, Konig, Haftseinsson, Jansen, & Stadelmann (2011) found that individuals from Iceland and Switzerland used less self-presentational behavior than people from the United States. Differences in self-presentation have also been found in job interviews involving individuals from Ghana, Turkey, Norway, and Germany, with the former two groups showing higher impression management scores than the latter two (Bye et al., 2011).
So far we have been talking about self-presentation as it operates in particular situations in the short-term. However, we also engage in longer-term self-presentational projects, where we seek to build particular reputations with particular audiences. Emler & Reicher (1995) describe the unique capacity humans have to know one another by repute and argue that, accordingly, we are often engaged in a process of reputation management, which is a form of long-term self-presentation, where individuals seek to build and sustain specific reputations with important audiences. According to this perspective, our behaviors in current social situations may not only be to serve our self-presentational goals in that moment, but also be based on a consideration of their longer-term repercussions for our reputations. As many politicians, for example, know only too well, a poor decision from their past can come back to haunt them when their reputation is being assessed during a campaign.
The concept of reputation management can be used to help explain a wide variety of social and antisocial behaviors, including corporate branding (Smith, Smith, & Wang, 2010), sociomoral debate (Emler, Tarry, & St. James, 2007), and teenage criminal activity (Lopez-Romero & Romero, 2011). In the last example, it is argued that a lot of teenage antisocial behavior results from a desire to build a reputation for toughness and rebelliousness with like-minded peer audiences (Emler & Reicher, 1995). Similarly, antisocial and self-destructive online actions, like people posting to Facebook their involvement in illegal acts during riots, or individuals engaging in life-threatening activities in Internet crazes like Neknominate, may make more sense if they are considered partly as stemming from a desire to project a particular reputation to specific audiences. Perhaps the perceived social kudos from doing these things outweighs the obvious personal risks in the individuals’ minds at the time.
People often project distinct reputations to different social audiences. For example, adolescents who engage in antisocial activity to build reputations for rebelliousness among their peers will often seek to construct very different reputations when their parents are the audience (Emler & Reicher, 1995). The desire to compartmentalize our reputations and audiences can even spill over into our online behaviors. Wiederhold (2012) found that, with some adolescents’ Facebook friends numbering in the hundreds or thousands, increasing numbers are moving to Twitter in order to reach a more selective audience. One critical trigger for this has been that their parents are now often friends with them on Facebook, creating a need for young people to find a new space where they can build reputations that may not always be parent-friendly (Wiederhold, 2012).
Although the desire to present the self favorably is a natural part of everyday life, both person and situation factors influence the extent to which we do it. For one, we are more likely to self-present in some situations than in others. When we are applying for a job or meeting with others whom we need to impress, we naturally become more attuned to the social aspects of the self, and our self-presentation increases.
There are also individual differences. Some people are naturally better at self-presentation—they enjoy doing it and are good at it—whereas others find self-presentation less desirable or more difficult. An important individual-difference variable known as self-monitoring has been shown in many studies to have a major impact on self-presentation. Self-monitoring refers to the tendency to be both motivated and capable of regulating our behavior to meet the demands of social situations (Gangestad & Snyder, 2000). High self-monitors are particularly good at reading the emotions of others and therefore are better at fitting into social situations—they agree with statements such as “In different situations and with different people, I often act like very different persons,” and “I guess I put on a show to impress or entertain people.” Low self-monitors, on the other hand, generally act on their own attitudes, even when the social situation suggests that they should behave otherwise. Low self-monitors are more likely to agree with statements such as “At parties and social gatherings, I do not attempt to do or say things that others will like,” and “I can only argue for ideas that I already believe.” In short, high self-monitors use self-presentation to try to get other people to like them by behaving in ways that the others find desirable, whereas low self-monitors tend to follow their internal convictions more than the demands of the social situation.
In one experiment that showed the importance of self-monitoring, Cheng and Chartrand (2003) had college students interact individually with another student (actually an experimental confederate) whom they thought they would be working with on an upcoming task. While they were interacting, the confederate subtly touched her own face several times, and the researchers recorded the extent to which the student participant mimicked the confederate by also touching his or her own face.
The situational variable was the status of the confederate. Before the meeting began, and according to random assignment to conditions, the students were told either that they would be the leader and that the other person would be the worker on the upcoming task, or vice versa. The person variable was self-monitoring, and each participant was classified as either high or low on self-monitoring on the basis of his or her responses to the self-monitoring scale.
As you can see in Figure 3.12, Cheng and Chartrand found an interaction effect: the students who had been classified as high self-monitors were more likely to mimic the behavior of the confederate when she was described as being the leader than when she was described as being the worker, indicating that they were “tuned in” to the social situation and modified their behavior to appear more positively. Although the low self-monitors did mimic the other person, they did not mimic her more when the other was high, versus low, status. This finding is consistent with the idea that the high self-monitors were particularly aware of the other person’s status and attempted to self-present more positively to the high-status leader. The low self-monitors, on the other hand—because they feel less need to impress overall—did not pay much attention to the other person’s status.
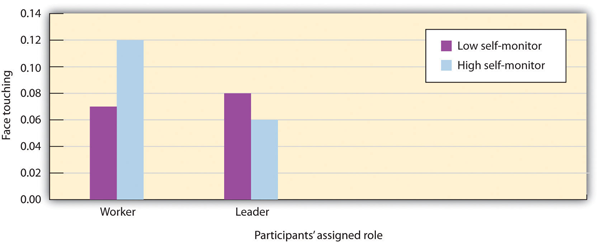
High self-monitors imitated more when the person they were interacting with was of higher (versus lower) status. Low self-monitors were not sensitive to the status of the other. Data are from Cheng and Chartrand (2003).
This differential sensitivity to social dynamics between high and low self-monitors suggests that their self-esteem will be affected by different factors. For people who are high in self-monitoring, their self-esteem may be positively impacted when they perceive that their behavior matches the social demands of the situation, and negatively affected when they feel that it does not. In contrast, low self-monitors may experience self-esteem boosts when they see themselves behaving consistently with their internal standards, and feel less self-worth when they feel they are not living up to them (Ickes, Holloway, Stinson, & Hoodenpyle, 2006).
Key Takeaways
- Our self-concepts are affected by others’ appraisals, as demonstrated by concepts including the looking-glass self and self-labeling.
- The self-concept and self-esteem are also often strongly influenced by social comparison. For example, we use social comparison to determine the accuracy and appropriateness of our thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
- When we are able to compare ourselves favorably with others through downward social comparison, we feel good about ourselves. Upward social comparison with others who are better off than we are leads to negative emotions.
- Social identity refers to the positive emotions that we experience as a member of an important social group.
- Normally, our group memberships result in positive feelings, which occur because we perceive our own groups, and thus ourselves, in a positive light.
- Which of our many category identities is most accessible for us will vary from day to day as a function of the particular situation we are in.
- In the face of others’ behaviors, we may enhance our self-esteem by “basking in the reflected glory” of our ingroups or of other people we know.
- If other people’s actions threaten our sense of self according to self-evaluation maintenance theory, we may engage in a variety of strategies aimed at redefining our self-concept and rebuilding our self-esteem.
- The tendency to present a positive self-image to others, with the goal of increasing our social status, is known as self-presentation, and it is a basic and natural part of everyday life. Different self-presentation strategies may be used to create different emotions in other people.
- We often use self-presentation in the longer term, seeking to build and sustain particular reputations with specific social audiences.
- The individual-difference variable of self-monitoring relates to the ability and desire to self-present.
Exercises and Critical Thinking
- Describe some aspects of your self-concept that have been created through social comparison.
- Describe times when you have engaged in downward and upward social comparison and the effects these comparisons have had on your self-esteem. To what extent do your experiences fit with the research evidence here?
- What are your most salient social identities? How do they create positive feelings for you?
- Outline a situation where someone else’s behavior has threatened your self-concept. Which of the strategies outlined in relation to self-evaluation maintenance theory did you engage in to rebuild your self-concept?
- Identify a situation where you basked in the reflected glory of your ingroup’s behavior or peformance. What effect did this have on your self-esteem and why?
- Describe some situations where people you know have used each of the self-presentation strategies that were listed in this section. Which strategies seem to be more and less effective in helping them to achieve their social goals, and why?
- Consider your own level of self-monitoring. Do you think that you are more of a high or a low self-monitor, and why? What do you see as the advantages and disadvantages for you of the level of self-monitoring that you have?
References
Baldwin, M. W., & Holmes, J. O. (1987). Salient private audiences and awareness of the self. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 52, 1087-1098.
Baumeister, R. F., Smart, L., & Boden, J. M. (1996). Relation of threatened egotism to violence and aggression: The dark side of high self-esteem. Psychological Review, 103(1), 5-33. doi:10.1037/0033-295X.103.1.5
Bauer, I., Wrosch, C., & Jobin, J. (2008). I’m better off than most other people: The role of social comparisons for coping with regret in young adulthood and old age. Psychology And Aging, 23(4), 800-811. doi:10.1037/a0014180
Bazarova, N. N., Taft, J. G., Choi, Y., & Cosley, D. (2013). Managing impressions and relationships on Facebook: Self-presentational and relational concerns revealed through the analysis of language style. Journal Of Language And Social Psychology, 32(2), 121-141. doi:10.1177/0261927X12456384
Beach, S. H., Tesser, A., Mendolia, M., Anderson, P., Crelia, R., Whitaker, D., & Fincham, F. D. (1996). Self-evaluation maintenance in marriage: Toward a performance ecology of the marital relationship. Journal of Family Psychology, 10(4), 379-396. doi:10.1037/0893-3200.10.4.379
Beer, A., Watson, D., & McDade-Montez, E. (2013). Self–other agreement and assumed similarity in neuroticism, extraversion, and trait affect: Distinguishing the effects of form and content. Assessment, 20(6), 723-737. doi:10.1177/1073191113500521
Blanton, H., Buunk, B. P., Gibbons, F. X., & Kuyper, H. (1999). When better-than-others compare upward: Choice of comparison and comparative evaluation as independent predictors of academic performance. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 76(3), 420–430.
Buunk, A. P., & Gibbons, F. X. (2007). Social comparison: The end of a theory and the emergence of a field. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 102(1), 3–21.
Buunk, B. P., Gibbons, F. X., & Buunk, A. P. (1997). Health, coping and well-being: Perspectives from social comparison theory. Psychology Press.
Buunk, A. P., Gibbons, F. X., & Visser, A. (2002). The relevance of social comparison processes for prevention and health care. Patient Education and Counseling, 47, 1–3.
Buunk, B. P., Zurriaga, R., Peiró, J. M., Nauta, A., & Gosalvez, I. (2005). Social comparisons at work as related to a cooperative social climate and to individual differences in social comparison orientation. Applied Psychology: An International Review, 54(1), 61-80. doi:10.1111/j.1464-0597.2005.00196.x
Bye, H., Sandal, G., van de Vijver, F. R., Sam, D., Çakar, N., & Franke, G. (2011). Personal values and intended self‐presentation during job interviews: A cross‐cultural comparison. Applied Psychology: An International Review, 60(1), 160-182. doi:10.1111/j.1464-0597.2010.00432.x
Carter, L. (2012). Locus of control, internalized heterosexism, experiences of prejudice, and the psychological adjustment of lesbian, gay, and bisexual individuals. Dissertation Abstracts International, 73.
Cheng, C., & Chartrand, T. L. (2003). Self-Monitoring Without Awareness: Using Mimicry as a Nonconscious Affiliation Strategy. Journal Of Personality And Social Psychology, 85(6), 1170-1179. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.85.6.1170
Cialdini, R. B., Borden, R. J., Thorne, A., Walker, M. R., Freeman, S., & Sloan, L. R. (1976). Basking in reflected glory: Three (football) field studies. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 34, 366–374.
Collins, R. L. (2000). Among the better ones: Upward assimilation in social comparison. In J. Suls & L. Wheeler (Eds.), Handbook of social comparison (pp. 159–172). New York, NY: Kulwer Academic/Plenum.
Cooley, C. H. (1902). Human nature and social order. New York: Scribner’s.
Deaux, K., Reid, A., Mizrahi, K., & Ethier, K. A. (1995). Parameters of social identity. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 68(2), 280–291.
Dovidio, J. F., Brown, C. E., Heltman, K., Ellyson, S. L., & Keating, C. F. (1988). Power displays between women and men in discussions of gender-linked tasks: A multichannel study. Journal Of Personality And Social Psychology, 55(4), 580-587. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.55.4.580
Eagly, A. H., & Carli, L. L. (2007). Through the labyrinth: The truth about how women become leaders. Boston, MA, US: Harvard Business School Press.
Emler, N. & Reicher, S. (1995). Adolescence and delinquency: The collective management of reputation. Malden Blackwell Publishing.
Emler, N., Tarry, H. & St. James, A. (2007). Postconventional moral reasoning and reputation. Journal of Research in Personality, 41, 76-89.
Feinstein, B. A., Hershenberg, R., Bhatia, V., Latack, J. A., Meuwly, N., & Davila, J. (2013). Negative social comparison on Facebook and depressive symptoms: Rumination as a mechanism. Psychology Of Popular Media Culture, 2(3), 161-170. doi:10.1037/a003311
Festinger, L. U. (1954). A theory of social comparison processes. Human Relations, 7, 117-140. doi: 10.1177/001872675400700202
Fox, J. D., & Stinnett, T. A. (1996). The effects of labeling bias on prognostic outlook for children as a function of diagnostic label and profession. Psychology In The Schools, 33(2), 143-152.
Friedlander, M. L., & Schwartz, G. S. (1985). Toward a theory of strategic self-presentation in counseling and psychotherapy. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 32(4), 483-501. doi: 10.10370022-0167.32.4.483
Galinsky, A. D., Wang, C. S., Whitson, J. A., Anicich, E. M., Hugenberg, K., & Bodenhausen, G. V. (2013). The reappropriation of stigmatizing labels: The reciprocal relationship between power and self-labeling. Psychological Science, 24(10), 2020-2029. doi:10.1177/0956797613482943
Gangestad, S. W., & Snyder, M. (2000). Self-monitoring: Appraisal and reappraisal. Psychological Bulletin, 126(4), 530-555. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.126.4.530
Goffman, E. (1959). The presentation of self in everyday life. Oxford, England: Doubleday.
Goldstein, N. J., Cialdini, R. B., & Griskevicius, V. (2008). A room with a viewpoint: Using social norms to motivate environmental conservation in hotels. Journal of Consumer Research, 35(3), 472-482.
Hardin, C., & Higgins, T. (1996). Shared reality: How social verification makes the subjective objective. In R. M. Sorrentino & E. T. Higgins (Eds.), Handbook of motivation and cognition: Foundations of social behavior (Vol. 3, pp. 28–84). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Helgeson, V. S., & Mickelson, K. (2000). Coping with chronic illness among the elderly: Maintaining self-esteem. In S. B. Manuck, R. Jennings, B. S. Rabin, & A. Baum (Eds.), Behavior, health, and aging. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Higgins, E. T., Loeb, I., & Moretti, M. (Eds.). (1995). Self-discrepancies and developmental shifts in vulnerability: Life transitions in the regulatory significance of others. Rochester, NY: University of Rochester Press.
Hogg, M. A. (2003). Social identity. In M. R. Leary, J. P. Tangney, M. R. E. Leary, & J. P. E. Tangney (Eds.), Handbook of self and identity (pp. 462–479). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Ickes, W., Holloway, R., Stinson, L. L., & Hoodenpyle, T. (2006). Self-Monitoring in Social Interaction: The Centrality of Self-Affect.Journal Of Personality, 74(3), 659-684. doi:10.1111/j.1467-6494.2006.00388.x
Jones, E. E., & Pittman, T. S. (1982). Toward a general theory of strategic self presentation. In J. Suls (Ed.), Psychological perspectives on the self. Hillsdale, NJ:Erlbaum
König, C. J., Hafsteinsson, L. G., Jansen, A., & Stadelmann, E. H. (2011). Applicants’ self‐presentational behavior across cultures: Less self‐presentation in Switzerland and Iceland than in the United States. International Journal Of Selection And Assessment,19(4), 331-339.
Kulik, J. A., Mahler, H. I. M., & Moore, P. J. (1996). Social comparison and affiliation under threat: Effects on recovery from major surgery. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 71(5), 967–979.
López-Romero, L., & Romero, E. (2011). Reputation management of adolescents in relation to antisocial behavior. The Journal of Genetic Psychology: Research And Theory On Human Development, 172(4), 440-446. doi:10.1080/00221325.2010.549156
Luhtanen, R., & Crocker, J. (1992). A collective self-esteem scale: Self-evaluation of one’s social identity. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 18, 302–318.
Marsh, H. W., Kong, C.-K., & Hau, K-T. (2000). Longitudinal multilevel models of the big-fish-little-pond effect on academic self-concept: Counterbalancing contrast and reflected-glory effects in Hong Kong schools. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 78, 337–349.
Marwick, A. E., & Boyd, D. (2011). I tweet honestly, I tweet passionately: Twitter users, context collapse, and the imagined audience. New Media & Society, 13(1), 114-133. doi:10.1177/1461444810365313
Mazur, E., & Kozarian, L. (2010). Self-presentation and interaction in blogs of adolescents and young emerging adults. Journal Of Adolescent Research, 25(1), 124-144. doi:10.1177/0743558409350498
Mehdizadeh, S. (2010). Self-presentation 2.0: Narcissism and self-esteem on Facebook. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, And Social Networking, 13(4), 357-364. doi:10.1089/cyber.2009.0257
Morse, S., & Gergen, K. (1970). Social comparison, self-consistency, and the concept of self. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 16(1), 148–156.
Moses, T. (2009). Self-labeling and its effects among adolescents diagnosed with mental disorders. Social Science and Medicine, 68(3), 570-578.
Nicholls, E., & Stukas, A. A. (2011). Narcissism and the self-evaluation maintenance model: Effects of social comparison threats on relationship closeness. The Journal of Social Psychology, 151(2), 201-212. doi:10.1080/00224540903510852
Oakes, P. J., Haslam, S. A., & Turner, J. C. (1994). Sterotyping and social reality. Oxford, England: Blackwell.
Perkins, K., Wiley, S., & Deaux, K. (2014). Through which looking glass? Distinct sources of public regard and self-esteem among first- and second-generation immigrants of color. Cultural Diversity And Ethnic Minority Psychology, 20(2), 213-219. doi:10.1037/a0035435
Schachter, S. (1959). The psychology of affiliation. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
Schlenker, B. R. (2003). Self-presentation. In M. R. Leary, J. P. Tangney, M. R. E. Leary, & J. P. E. Tangney (Eds.), Handbook of self and identity (pp. 492–518). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Siero, F. W., Bakker, A. B., Dekker, G. B., & van den Berg, M. T. (1996). Changing organizational energy consumption behavior through comparative feedback. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 16, 235-246.
Smith, K., Smith, M., & Wang, K. (2010). Does brand management of corporate reputation translate into higher market value?. Journal of Strategic Marketing, 18(3), 201-221. doi:10.1080/09652540903537030
Snyder, C., Cheavens, J., & Sympson, S. (1997). Hope: An individual motive for social commerce. Group Dynamics: Theory, Research, and Practice, 1, 107–118.
Strauman, T. J., & Higgins, E. T. (1988). Self-discrepancies as predictors of vulnerability to distinct syndromes of chronic emotional distress. Journal of Personality, 56(4), 685–707.
Szymanski, D. M., & Obiri, O. (2011). Do religious coping styles moderate or mediate the external and internalized racism-distress links? The Counseling Psychologist, 39(3), 438-462. doi:10.1177/0011000010378895
Tajfel, H. (1981). Human groups and social categories: Studies in social psychology. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
Taylor, L.M., Hume, I.R., and Welsh, N. (2010) Labelling and Self-esteem: The impact of using specific versus generic labels. Educational Psychology, 1, 1-12
Tesser, A. (1980) Self–esteem maintenance in family dynamics. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 1980, 39(1),
Tesser, A. (1988). Toward a self-evaluation maintenance model of social behavior. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 21, 181–227.
Toma, C. L., Hancock, J. T., & Ellison, N. B. (2008). Separating fact from fiction: An examination of deceptive self-presentation in online dating profiles. Personality And Social Psychology Bulletin, 34(8), 1023-1036. doi:10.1177/0146167208318067
Van Lange, P. A. M. (2008). Social comparison is basic to social psychology. American Journal of Psychology, 121(1), 169–172.
Vrugt, A., & Koenis, S. (2002). Perceived self-efficacy, personal goals, social comparison, and scientific productivity. Applied Psychology: An International Review, 51(4), 593–607.
Wang, S., & Stefanone, M. A. (2013). Showing off? Human mobility and the interplay of traits, self-disclosure, and Facebook check-ins. Social Science Computer Review, 31(4), 437-457.
White, K., & Lehman, D. R. (2005). Culture and social comparison seeking: The role of self-motives. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 31, 232-242.
Wiederhold, B. K. (2012). As parents invade Faceboo, teens tweet more. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 15(8), 385-386.
Wosinska, W., Dabul, A. J., Whetstone-Dion, R., & Cialdini, R. B. (1996). Self-presentational responses to success in the organization: The costs and benefits of modesty. Basic And Applied Social Psychology, 18(2), 229-242. doi:10.1207/s15324834basp1802_8
Yakushko, O., Davidson, M., & Williams, E.N. (2009). Identity Salience Model: A paradigm for integrating multiple identities in clinical practice. Psychotherapy: Theory, Research, Practice, Training 46, 180-192. doi: 10.1037/a0016080
Yeung, K., & Martin, J. (2003). The Looking Glass Self: An empirical test and elaboration. Social Forces, 81(3), 843-879. doi:10.1353/sof.2003.0048
- 30321 reads






