One of the reasons that people may hold stereotypes and prejudices is that they view the members of outgroups as different from them. We may become concerned that our interactions with people from different racial groups will be unpleasant, and these anxieties may lead us to avoid interacting with people from those groups (Mallett, Wilson, & Gilbert, 2008). What this suggests is that a good way to reduce prejudice is to help people create closer connections with members of different groups. People will be more favorable toward others when they learn to see those other people as more similar to them, as closer to the self, and to be more concerned about them.
The idea that intergroup contact will reduce prejudice, known as the contact hypothesis, is simple: If children from different ethnic groups play together in school, their attitudes toward each other should improve. And if we encourage college students to travel abroad, they will meet people from other cultures and become more positive toward them.
One important example of the use of intergroup contact to influence prejudice came about as a result of the important U.S. Supreme Court case Brown v. Board of Education in 1954. In this case, the U.S. Supreme Court agreed, based in large part on the testimony of psychologists, that busing Black children to schools attended primarily by White children, and vice versa, would produce positive outcomes on intergroup attitudes, not only because it would provide Black children with access to better schools, but also because the resulting intergroup contact would reduce prejudice between Black and White children. This strategy seemed particularly appropriate at the time it was implemented because most schools in the United States then were highly segregated by race.
The strategy of busing was initiated after the Supreme Court decision, and it had a profound effect on schools in the United States. For one, the policy was very effective in changing school makeup—the number of segregated schools decreased dramatically during the 1960s after the policy was begun. Busing also improved the educational and occupational achievement of Blacks and increased the desire of Blacks to interact with Whites; for instance, by forming cross-race friendships (Stephan, 1999). Overall, then, the case of desegregating schools in the United States supports the expectation that intergroup contact, at least in the long run, can be successful in changing attitudes. Nevertheless, as a result of several subsequent U.S. Supreme Court decisions, the policy of desegregating schools via busing was not continued past the 1990s.
Although student busing to achieve desegregated schools represents one prominent example of intergroup contact, such contact occurs in many other areas as well. Taken together, there is substantial support for the effectiveness of intergroup contact in improving group attitudes in a wide variety of situations, including schools, work organizations, military forces, and public housing. Pettigrew and Tropp (2006) conducted a meta-analysis in which they reviewed over 500 studies that had investigated the effects of intergroup contact on group attitudes. They found that attitudes toward groups that were in contact became more positive over time. Furthermore, positive effects of contact were found on both stereotypes and prejudice and for many different types of contacted groups.
The positive effects of intergroup contact may be due in part to increases in other-concern. Galinsky and Moskowitz (2000) found that leading students to take the perspective of another group member—which increased empathy and closeness to the person—also reduced prejudice. And the behavior of students on college campuses demonstrates the importance of connecting with others and the dangers of not doing so. Sidanius, Van Laar, Levin, and Sinclair (2004) found that students who joined exclusive campus groups, including fraternities, sororities, and minority ethnic organizations (such as the African Student Union), were more prejudiced to begin with and became even less connected and more intolerant of members of other social groups over the time that they remained in the organizations. It appears that memberships in these groups focused the students on themselves and other people who were very similar to them, leading them to become less tolerant of others who are different.
Although intergroup contact does work, it is not a panacea because the conditions necessary for it to be successful are frequently not met. Contact can be expected to work only in situations that create the appropriate opportunities for change. For one, contact will only be effective if it provides information demonstrating that the existing stereotypes held by the individuals are incorrect. When we learn more about groups that we didn’t know much about before, we learn more of the truth about them, leading us to be less biased in our beliefs. But if our interactions with the group members do not allow us to learn new beliefs, then contact cannot work.
When we first meet someone from another category, we are likely to rely almost exclusively on our stereotypes (Brodt & Ross, 1998). However, when we get to know the individual well (e.g., as a student in a classroom learns to know the other students over a school year), we may get to the point where we ignore that individual’s group membership almost completely, responding to him or her entirely at the individual level (Madon et al., 1998). Thus contact is effective in part because it leads us to get past our perceptions of others as group members and to individuate them.
When we get past group memberships and focus more on the individuals in the groups, we begin to see that there is a great deal of variability among the group members and that our global and undifferentiating group stereotypes are actually not that informative (Rothbart & John, 1985). Successful intergroup contact tends to reduce the perception of outgroup homogeneity. Contact also helps us feel more positively about the members of the other group, and this positive affect makes us like them more.
Intergroup contact is also more successful when the people involved in the contact are motivated to learn about the others. One factor that increases this motivation is interdependence—a state in which the group members depend on each other for successful performance of the group goals (Neuberg & Fiske, 1987). The importance of interdependence can be seen in the success of cooperative learning techniques, such as the jigsaw classroom (Aronson, Blaney, Stephan, Sikes, & Snapp, 1978; Aronson, 2004).
The jigsaw classroom is an approach to learning in which students from different racial or ethnic groups work together, in an interdependent way, to master material. The class is divided into small learning groups, where each group is diverse in ethnic and gender composition. The assigned material to be learned is divided into as many parts as there are students in the group, and members of different groups who are assigned the same task meet together to help develop a strong report. Each student then learns his or her own part of the material and presents this piece of the puzzle to the other members of his or her group. The students in each group are therefore interdependent in learning all the material. A wide variety of techniques, based on principles of the jigsaw classroom, are in use in many schools around the world, and research studying these approaches has found that cooperative, interdependent experiences among students from different social groups are effective in reducing negative stereotyping and prejudice (Stephan, 1999).
In sum, we can say that contact will be most effective when it is easier to get to know, and become more respectful of, the members of the other group and when the social norms of the situation promote equal, fair treatment of all groups. If the groups are treated unequally, for instance, by a teacher or leader who is prejudiced and who therefore treats the different groups differently, or if the groups are in competition rather than cooperation, there will be no benefit. In cases when these conditions are not met, contact may not be effective and may in fact increase prejudice, particularly when it confirms stereotypical expectations (Stangor, Jonas, Stroebe, & Hewstone, 1996). Finally, it is important that enough time be allowed for the changes to take effect. In the case of busing in the United States, for instance, the positive effects of contact seemed to have been occurring, but they were not happening particularly fast.
Let’s consider (in the following Research Focus) still another way that intergroup contact can reduce prejudice—the idea that prejudice can be reduced for people who have friends who are friends with members of the outgroup, known as the extended-contact hypothesis.
Research Focus: The Extended-Contact Hypothesis
Although the contact hypothesis proposes that direct contact between people from different social groups will produce more positive attitudes between them, recent evidence suggests that
prejudice can also be reduced for people who have friends who are friends with members of the outgroup, even if the individual does not have direct contact with the outgroup members himself
or herself. This hypothesis is known as the extended-contact hypothesis. Supporting this prediction, Wright, Aron, McLaughlin-Volpe, and Ropp (1997) found in two correlational studies that
college students who reported that their own friends had friends who were from another ethnic group reported more positive attitudes toward that outgroup than did students who did not have
any friends who had outgroup friends, even controlling for the participants’ own outgroup friendships.
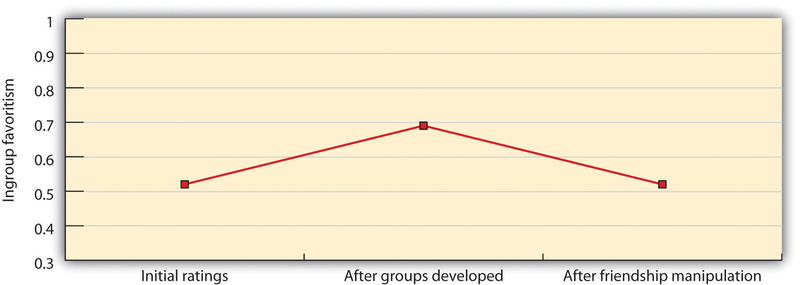
Wright and his colleages (1997) also tested the extended-contact hypothesis experimentally. Participants were four groups of 14 students, and each group spent a whole day in the lab. On
arrival, seven participants were assigned to the “green” group, and seven to the “blue” group, supposedly on the basis of similar interests. To create strong ingroup identity and to produce
competition between the groups, the group members wore blue and green T-shirts and engaged in a series of competitive tasks. Participants then expressed their initial thoughts and feelings
about the outgroup and its members. Then, supposedly as part of an entirely different study, one participant was randomly selected from each group, and the two were taken to a separate room
in which they engaged in a relationship-building task that has been shown to quickly create feelings of friendship between two strangers. Then the two members from each team were then
reunited with their original groups, where they were encouraged to describe their experience with the other group member in the friendship-building task. In the final phase, the groups then
engaged in another competitive task, and participants rated their thoughts and feelings about the outgroup and its members again. As you can see in Figure 11.10, and supporting the
extended-contact hypothesis, results showed that the participants (including those who did not participate in the closeness task themselves) were more positive toward the outgroup after than
before the two team members had met. This study, as well as many other studies, supports the importance of cross-group friendships in promoting favorable outgroup attitudes (Page-Gould,
Mendoza-Denton, & Tropp, 2008; Shook & Fazio, 2008).
- 7112 reads






