We have seen that the experience of cognitive dissonance can influence our thoughts and feelings about an attitude object by making us feel uncomfortable about our own behaviors. The discrepant behavior causes our sense of self-worth to be lowered, which then causes us to change our attitudes to feel better about ourselves.
- Discrepant behavior → lowered self-worth → changes in thoughts and feelings
Imagine that immediately after you did something dishonest, but before you had a chance to try to reduce the dissonance you were experiencing, you were able to remind yourself of the fact that you had recently done something else very positive—perhaps you had recently spent some time volunteering at a homeless shelter or gotten a really high score on an important exam. Would the possibility of boosting your self-esteem in this other, but unrelated, domain make it unnecessary for you to engage in dissonance reduction? Could you say, “Well, it’s true that I cheated, but I’m really a fine, intelligent, and generous person.” Research has demonstrated that this is the case. If we can affirm our self-worth, even on dimensions that are not related to the source of the original dissonance, the negative feelings we experience are reduced and so is the tendency to justify our attitudes (Steele, 1988).
Just as finding ways to affirm our self-esteem should reduce cognitive dissonance, threats to our self-esteem should increase it. Because cognitive dissonance poses a threat to one’s self-esteem, people who are more motivated by self-concern should show bigger changes in their thoughts and feelings after they engage in a discrepant behavior than should those who are less motivated by self-concern.
Following the research of Brehm (1956), Heine and Lehman (1997) conducted an experiment to determine if threats to self-esteem would increase the magnitude of the dissonance-reduction effect, and if dissonance reduction would also occur for Japanese students as they had previously been found in students from Western samples. They expected that there would be less need for dissonance reduction in the Japanese than in Western students because the Japanese (and other Easterners) were less motivated overall to maintain a positive self-image.
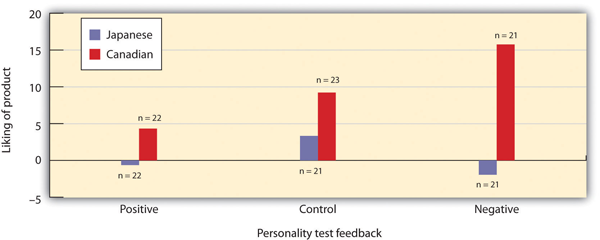
In their study, 71 Canadian and 71 Japanese participants were first asked to take a personality test. According to random assignment to conditions, one-third of the sample in each country were led to believe that they had scored much higher on the test than did the other participants and thus that they had “positive” personalities (the positive feedback condition). Another third of the sample (the negative feedback condition) were led to believe that they had scored more poorly on the test than average, and the final third (the control condition) were not given any feedback on their personality test scores.
Then all participants rated the desirability of 10 compact discs (which were known to be popular in both Canada and Japan) and were asked to choose between their fifth- and sixth-rated CDs as compensation for their participation. Finally, after choosing one of the CDs, the participants were asked to again rate their liking for the CDs. The change in the ratings from before choice to after choice, which would have occurred if the participants increased their liking of the CD they had chosen or decreased their liking of the CD they had rejected, was the dependent measure in the study.
As you can see in Figure 4.12, the researchers found a significant interaction between culture and personality feedback. The pattern of means showed that the feedback mattered for the Canadian participants—the difference in the ratings of the chosen versus the rejected CD (the “spread of alternatives”) increased from the positive to the control to the negative feedback conditions. However, there was no significant simple effect of feedback for the Japanese students, nor did they show a significant spread of alternatives in any feedback condition.
However, other researchers have found that individuals from collectivistic cultures do show dissonance effects when they are focused on their relationships with others. For instance, Kitayama, Snibbe, Markus, and Suzuki (2004) found that East Asian participants experienced dissonance particularly when they were asked to think about a close friend who had made a dissonance-creating decision. Such a result would be expected because behaviors that involve more other-oriented, collectivistic outcomes should be more important for these people. Indeed, research has found that advertisements that are framed in terms of personal benefits (e.g., “Use this breath mint!”) are more persuasive in individualistic cultures, whereas ads that emphasize family or ingroup benefits (e.g., “Share this breath mint with your friends!”) are more persuasive in collectivistic cultures (Han & Shavitt, 1994).
Although dissonance is most likely when our behavior violates our positive self-concept, attitude change can occur whenever our thoughts and behaviors are inconsistent, even if the self-concept is not involved. For instance, Harmon-Jones and his colleagues (Harmon-Jones, Brehm, Greenberg, Simon, & Nelson, 1996) had people drink an unpleasant-tasting beverage (Kool-Aid made with vinegar instead of sugar) and then write down on a small slip of paper, which they then immediately crumpled up and threw away, a statement saying that they really liked the drink. Harmon-Jones and his colleagues found that even though the lie could not possibly harm anyone, the act of lying nevertheless made the participants express more positive attitudes toward the drink. It appears that even lying to oneself about something relatively unimportant can produce dissonance and change attitudes (Prislin & Pool, 1996; Stone, 1999).
Salespeople make use of psychological principles, including self-perception and cognitive dissonance, to encourage people to buy their products, often in ways that seem less than completely open and ethical. Informed consumers are aware of such techniques, including the foot-in-the-door technique, the low-ball technique, and the bait-and-switch technique. Let’s consider in the next section how these strategies might work.
- 6904 reads






