In order to be effective persuaders, we must first get people’s attention, then send an effective message to them, and then ensure that they process the message in the way we would like them to. Furthermore, to accomplish these goals, persuaders must consider the cognitive, affective, and behavioral aspects of their methods. Persuaders also must understand how the communication they are presenting relates to the message recipient—his or her motivations, desires, and goals.
Research has demonstrated that the same message will be more effective if is delivered by a more persuasive communicator. In general, we can say that communicators are more effective when they help their recipients feel good about themselves—that is, by appealing to self-concern. For instance, attractive communicators are frequently more effective persuaders than are unattractive communicators. Attractive communicators create a positive association with the product they are trying to sell and put us in a good mood, which makes us more likely to accept their messages. And as the many marketers who include free gifts, such as mailing labels or small toys, in their requests for charitable donations well know, we are more likely to respond to communicators who offer us something personally beneficial.
We’re also more persuaded by people who are similar to us in terms of opinions and values than by those whom we perceive as being different. This is of course why advertisements targeted at teenagers frequently use teenagers to present the message, and why advertisements targeted at the elderly use older communicators.
When communicators are perceived as attractive and similar to us, we tend to like them. And we also tend to trust the people that we like. The success of Tupperware parties, in which friends get together to buy products from other friends, may be due more to the fact that people like the “salesperson” than to the nature of the product. People such as the media mogul Oprah Winfrey, tennis star Roger Federer, and the musician Bono have been used as communicators for products in part because we see them as trustworthy and thus likely to present an unbiased message. Trustworthy communicators are effective because they allow us to feel good about ourselves when we accept their message, often without critically evaluating its content (Priester & Petty, 2003).

Expert communicators may sometimes be perceived as trustworthy because they know a lot about the product they are selling. When a doctor recommends that we take a particular drug, we are likely to be influenced because we know that he or she has expertise about the effectiveness of drugs. It is no surprise that advertisers use race car drivers to sell cars and basketball players to sell athletic shoes.
Although expertise comes in part from having knowledge, it can also be communicated by how one presents a message. Communicators who speak confidently, quickly, and in a straightforward way are seen as more expert than those who speak in a more hesitating and slower manner. Taking regular speech and speeding it up by deleting very small segments of it, so that it sounds the same but actually goes faster, makes the same communication more persuasive (MacLachlan & Siegel, 1980; Moore, Hausknecht, & Thamodaran, 1986). This is probably in part because faster speech makes the communicator seem more like an expert but also because faster speech reduces the listener’s ability to come up with counterarguments as he or she listens to the message (Megehee, Dobie, & Grant, 2003). Effective speakers frequently use this technique, and some of the best persuaders are those who speak quickly.
Expert communicators are expected to know a lot about the product they are endorsing, but they may not be seen as trustworthy if their statements seem to be influenced by external causes. People who are seen to be arguing in their own self-interest (e.g., an expert witness who is paid by the lawyers in a case; a celebrity who is paid to endorse a product) may be ineffective because we may discount their communications (Eagly, Wood, & Chaiken, 1978; Wood & Eagly, 1981). On the other hand, when a person presents a message that goes against external causes, for instance, by arguing in favor of an opinion to a person who is known to disagree with it, we see the internal states (that the individual really believes in the message he or she is expressing) as even more powerful.
Communicators also may be seen as biased if they present only one side of an issue while completely ignoring the potential problems or counterarguments to the message. In these cases, people who are informed about both sides of the topic may see the communicator as attempting to unfairly influence them.
Although we are generally very aware of the potential that communicators may deliver messages that are inaccurate or designed to influence us, and we are able to discount messages that come from sources that we do not view as trustworthy, there is one interesting situation in which we may be fooled by communicators. This occurs when a message is presented by someone whom we perceive as untrustworthy. When we first hear that person’s communication, we appropriately discount it, and it therefore has little influence on our opinions. However, over time there is a tendency to remember the content of a communication to a greater extent than we remember the source of the communication. As a result, we may forget over time to discount the remembered message. This attitude change that occurs over time is known as the sleeper effect (Kumkale & Albarracín, 2004).
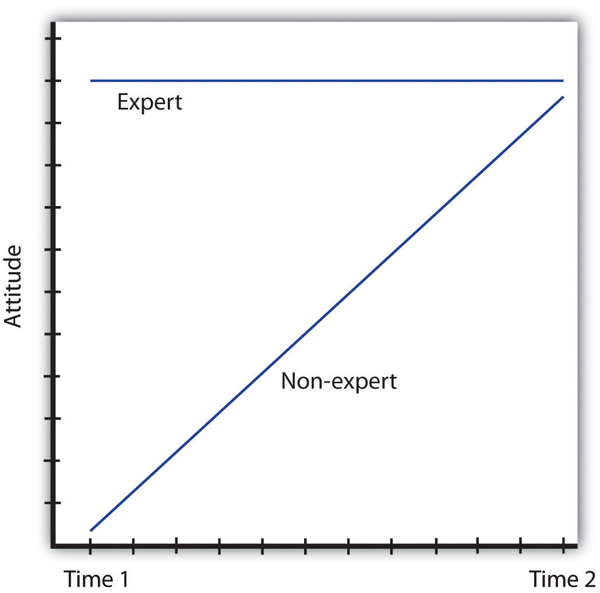
Perhaps you’ve experienced the sleeper effect. During high-profile election campaigns, candidates sometimes produce advertisements that attack their opponents. These kinds of communications occasionally stretch the truth in order to win public favor, which is why many people listen to them with a grain of salt. The trouble occurs, however, when people remember the claims made but forget the source of the communication. The sleeper effect is diagrammed in Figure 4.5.
- 4751 reads






