The most ubiquitous and important signal in electrical engineering is the sinusoid.
Sine Definition
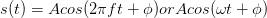
A is known as the sinusoid's amplitude, and determines the sinusoid's size. The amplitude conveys the sinusoid's physical
units (volts, lumens, etc). The frequencyf has units of Hz (Hertz) or s-1, and determines how rapidly
the sinusoid oscillates per unit time. The temporal variable t always has units of seconds, and thus the frequency determines how many oscillations/second
the sinusoid has. AM radio stations have carrier frequencies of about 1 MHz (one mega-hertz or 106 Hz), while FM stations have carrier frequencies of about 100 MHz. Frequency can also be
expressed by the symbol ω, which has units of radians/second. Clearly, 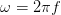 .
In communications, we most often express frequency in Hertz. Finally, φ is the phase, and determines the sine wave's behavior at the origin (t =0). It has units of
radians, but we can express it in degrees, realizing that in computations we must convert from degrees to radians. Note that if
.
In communications, we most often express frequency in Hertz. Finally, φ is the phase, and determines the sine wave's behavior at the origin (t =0). It has units of
radians, but we can express it in degrees, realizing that in computations we must convert from degrees to radians. Note that if 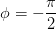 , the sinusoid corresponds to a sine function, having a zero value at the origin.
, the sinusoid corresponds to a sine function, having a zero value at the origin.
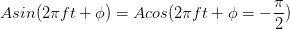
Thus, the only difference between a sine and cosine signal is the phase; we term either a sinusoid.
We can also define a discrete-time variant of the sinusoid: 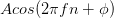 . Here,
the independent variable is n and represents the integers. Frequency now has no dimensions, and takes on values between 0 and 1.
. Here,
the independent variable is n and represents the integers. Frequency now has no dimensions, and takes on values between 0 and 1.
Exercise 1.4.1
Show that cos (2πfn) = cos (2π (f + 1) n), which means that a sinusoid having a frequency larger than one corresponds to a sinusoid having a frequency less than one.
Exercise 1.4.2
Can you think of a simple signal that has a finite number of values but is defined in continuous time? Such a signal is also an analog signal.
- 5561 reads






