A second kind of reliability is internal consistency, which is the consistency of people’s responses across the items on a multiple-item measure. In general, all the items on such measures are supposed to reflect the same underlying construct, so people’s scores on those items should be correlated with each other. On the Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale, people who agree that they are a person of worth should tend to agree that that they have a number of good qualities. If people’s responses to the different items are not correlated with each other, then it would no longer make sense to claim that they are all measuring the same underlying construct. This is as true for behavioral and physiological measures as for self-report measures. For example, people might make a series of bets in a simulated game of roulette as a measure of their level of risk seeking. This measure would be internally consistent to the extent that individual participants’ bets were consistently high or low across trials.
Like test-retest reliability, internal consistency can only be assessed by collecting and analyzing data. One approach is to look at a split-half correlation. This involves splitting the items into two sets, such as the first and second halves of the items or the even- and odd-numbered items. Then a score is computed for each set of items, and the relationship between the two sets of scores is examined. For example, Figure 5.3 shows the split-half correlation between several college students’ scores on the even-numbered items and their scores on the odd-numbered items of the Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale. Pearson’s rfor these data is +.88. A split-half correlation of +.80 or greater is generally considered good internal consistency.
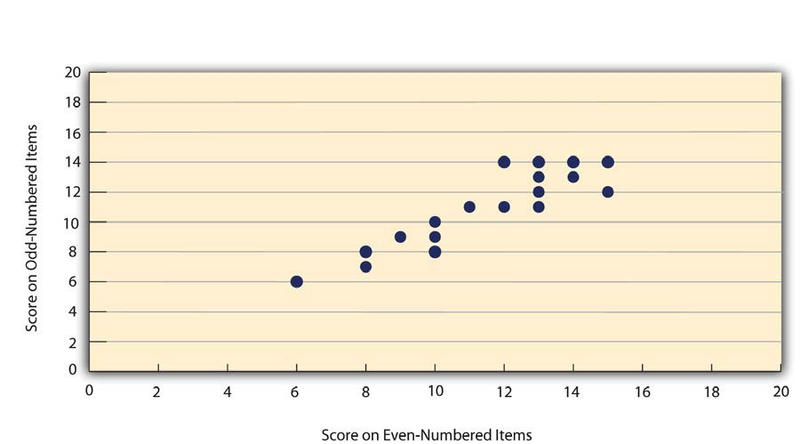
Perhaps the most common measure of internal consistency used by researchers in psychology is a statistic called Cronbach’s α (the Greek letter alpha). Conceptually, α is the mean of all possible split-half correlations for a set of items. For example, there are 252 ways to split a set of 10 items into two sets of five. Cronbach’s α would be the mean of the 252 split-half correlations. Note that this is not how α is actually computed, but it is a correct way of interpreting the meaning of this statistic. Again, a value of +.80 or greater is generally taken to indicate good internal consistency.
- 2955 reads






