A variant of the pretest-posttest design is the interrupted time-series design. A time series is a set of measurements taken at intervals over a period of time. For example, a manufacturing company might measure its workers’ productivity each week for a year. In an interrupted time series-design, a time series like this is “interrupted” by a treatment. In one classic example, the treatment was the reduction of the work shifts in a factory from 10 hours to 8 hours (Cook & Campbell, 1979). 1 Because productivity increased rather quickly after the shortening of the work shifts, and because it remained elevated for many months afterward, the researcher concluded that the shortening of the shifts caused the increase in productivity. Notice that the interrupted time-series design is like a pretest-posttest design in that it includes measurements of the dependent variable both before and after the treatment. It is unlike the pretest-posttest design, however, in that it includes multiple pretest and posttest measurements.
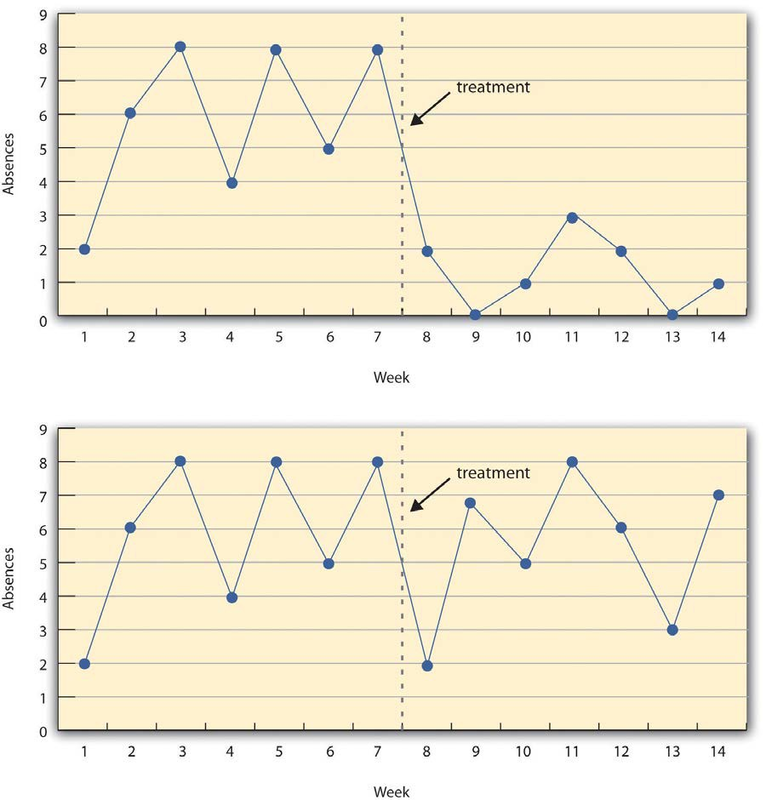
Figure 7.3 shows data from a hypothetical interrupted time-series study. The dependent variable is the number of student absences per week in a research methods course. The treatment is that the instructor begins publicly taking attendance each day so that students know that the instructor is aware of who is present and who is absent. The top panel of Figure 7.3 shows how the data might look if this treatment worked. There is a consistently high number of absences before the treatment, and there is an immediate and sustained drop in absences after the treatment. The bottom panel of Figure 7.3 shows how the data might look if this treatment did not work. On average, the number of absences after the treatment is about the same as the number before. This figure also illustrates an advantage of the interrupted time-series design over a simpler pretest-posttest design.
If there had been only one measurement of absences before the treatment at Week 7 and one afterward at Week 8, then it would have looked as though the treatment were responsible for the reduction. The multiple measurements both before and after the treatment suggest that the reduction between Weeks 7 and 8 is nothing more than normal week-to-week variation.
- 5812 reads






