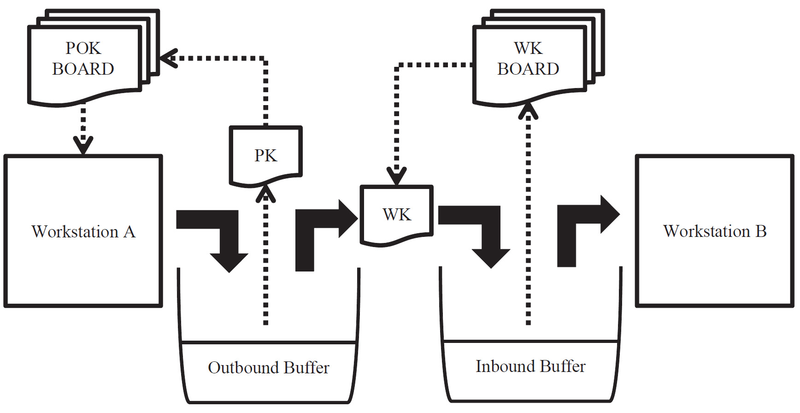
In the two-card system, each workstation has separate inbound and outbound buffers1, 2. Two different types of cards are used: Production Order Kanbans (POK) and Withdrawal Kanbans (WK). A WK contains information on how much material (raw materials / semi-finished materials) the succeeding process should withdraw. A schematic diagram of a two-card system is shown in Figure 6.2.
Each work-in-progress (WIP) container in the inbound buffer has a WK attached, as well as each WIP in the outbound buffer has a POK. WK and POK are paired, i.e. each given part number is always reported both in n POK and n WK. When a container is withdrawn from the inbound buffer, the B operator posts the WK on the WK board. Then, a warehouse-keeper operator uses the WK board as a picking list to replenish the inbound buffer: he takes the WK off the board and look for the paired POK in the outbound buffer. Then, he moves the corresponding quantity of the indicated material from the A outbound to the B inbound buffer, while exchanging the related POK with the WK on the container, restoring the initial situation. Finally, he posts the left POK on the POK board. Hence, like in the previous scenario, A workstation operator knows that one container of that kind must be replenished in the outbound stock buffer. The effectiveness of this simple technique – which was described in details by several authors3, 4, 5, 6 – is significantly influenced by the policy followed to determine the kanban processing order, in the boards.
- 17113 reads






