DNA has a double-helical structure (Figure 2.23 ). It is composed of two strands, or polymers, of nucleotides. The strands are formed with bonds between phosphate and sugar groups of adjacent nucleotides. The strands are bonded to each other at their bases with hydrogen bonds, and the strands coil about each other along their length, hence the “double helix” description, which means a double spiral.
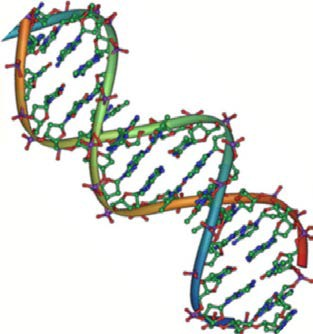
The alternating sugar and phosphate groups lie on the outside of each strand, forming the backbone of the DNA. The nitrogenous bases are stacked in the interior, like the steps of a staircase, and these bases pair; the pairs are bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. The bases pair in such a way that the distance between the backbones of the two strands is the same all along the molecule.
- 3028 reads






