The fermentation method used by animals and some bacteria like those in yogurt is lactic acid fermentation (Figure 4.16). This occurs routinely in mammalian red blood cells and in skeletal muscle that has insufficient oxygen supply to allow aerobic respiration to continue (that is, in muscles used to the point of fatigue). In muscles, lactic acid produced by fermentation must be removed by the blood circulation and brought to the liver for further metabolism. The chemical reaction of lactic acid fermentation is the following:
Pyruvic acid + NADH ↔ lactic acid + 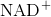
The enzyme that catalyzes this reaction is lactate dehydrogenase. The reaction can proceed in either direction, but the left-to-right reaction is inhibited by acidic conditions. This lactic acid build-up causes muscle stiffness and fatigue. Once the lactic acid has been removed from the muscle and is circulated to the liver, it can be converted back to pyruvic acid and further catabolized for energy.
Art Connection
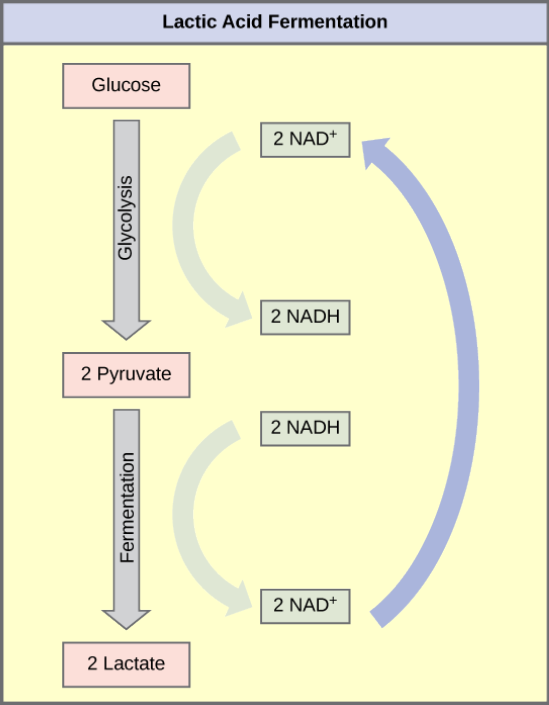
Tremetol, a metabolic poison found in white snake root plant, prevents the metabolism of lactate. When cows eat this plant, Tremetol is concentrated in the milk. Humans who consume the milk become ill. Symptoms of this disease, which include vomiting, abdominal pain, and tremors, become worse after exercise. Why do you think this is the case?
- 5065 reads






