Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Identify the two major abiotic factors that determine the type of terrestrial biome in an area
- Recognize distinguishing characteristics of each of the eight major terrestrial biomes
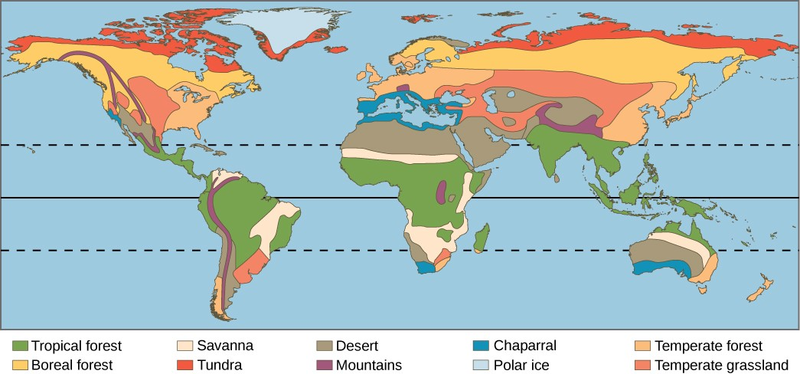
Earth’s biomes can be either terrestrial or aquatic. Terrestrial biomes are based on land, while aquatic biomes include both ocean and freshwater biomes. The eight major terrestrial biomes on Earth are each distinguished by characteristic temperatures and amount of precipitation. Annual totals and fluctuations of precipitation affect the kinds of vegetation and animal life that can exist in broad geographical regions. Temperature variation on a daily and seasonal basis is also important for predicting the geographic distribution of a biome. Since a biome is defined by climate, the same biome can occur in geographically distinct areas with similar climates (Figure 20.18). There are also large areas on Antarctica, Greenland, and in mountain ranges that are covered by permanent glaciers and support very little life. Strictly speaking, these are not considered biomes and in addition to extremes of cold, they are also often deserts with very low precipitation.
- 5816 reads






