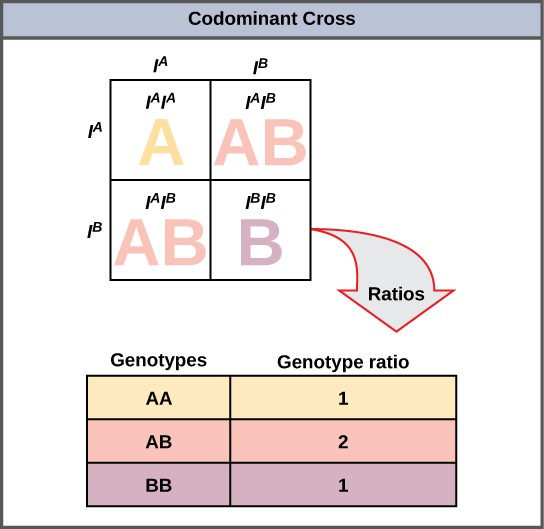
A variation on incomplete dominance is codominance, in which both alleles for the same characteristic are simultaneously expressed in the heterozygote. An example of
codominance occurs in the ABO blood groups of humans. The A and B alleles are expressed in the form of A or B molecules present on the surface of red blood cells. Homozygotes ( ) express either the A or the B phenotype, and
heterozygotes (
) express either the A or the B phenotype, and
heterozygotes ( ) express both phenotypes equally. The
) express both phenotypes equally. The  individual has blood type AB. In a self- cross between heterozygotes
expressing a codominant trait, the three possible offspring genotypes are phenotypically distinct. However, the 1:2:1 genotypic ratio characteristic of a Mendelian monohybrid cross still
applies (Figure 8.13).
individual has blood type AB. In a self- cross between heterozygotes
expressing a codominant trait, the three possible offspring genotypes are phenotypically distinct. However, the 1:2:1 genotypic ratio characteristic of a Mendelian monohybrid cross still
applies (Figure 8.13).
- 7223 reads






