Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Identify the shared characteristics of the natural sciences
- Understand the process of scientific inquiry
- Compare inductive reasoning with deductive reasoning
- Describe the goals of basic science and applied science
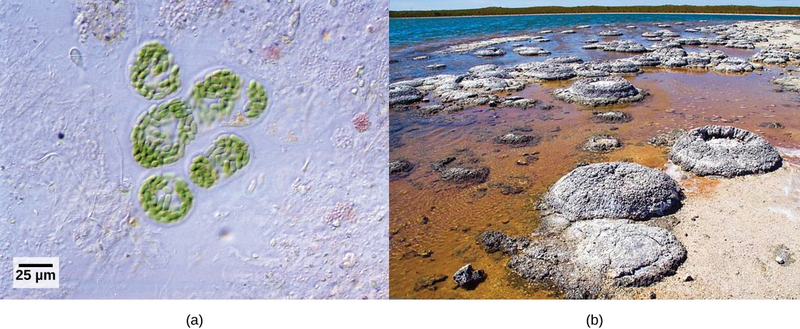
Like geology, physics, and chemistry, biology is a science that gathers knowledge about the natural world. Specifically, biology is the study of life. The discoveries of biology are made by a community of researchers who work individually and together using agreed-on methods. In this sense, biology, like all sciences is a social enterprise like politics or the arts. The methods of science include careful observation, record keeping, logical and mathematical reasoning, experimentation, and submitting conclusions to the scrutiny of others. Science also requires considerable imagination and creativity; a well-designed experiment is commonly described m as elegant, or beautiful. Like politics, science has considerable practical implications and some science is dedicated to practical applications, such as the prevention of disease (see Figure 1.15). Other science proceeds largely motivated by curiosity. Whatever its goal, there is no doubt that science, including biology, has transformed human existence and will continue to do so.
- 4918 reads






