The adult, or sporophyte, phase is the main phase in an angiosperm’s life cycle. Like gymnosperms, angiosperms are heterosporous. They produce microspores, which develop into pollen grains (the male gametophytes), and megaspores, which form an ovule containing the female gametophytes. Inside the anthers’ microsporangia (Figure 14.26), male microsporocytes divide by meiosis, generating haploid microspores that undergo mitosis and give rise to pollen grains. Each pollen grain contains two cells: one generative cell that will divide into two sperm, and a second cell that will become the pollen tube cell.
Art Connection
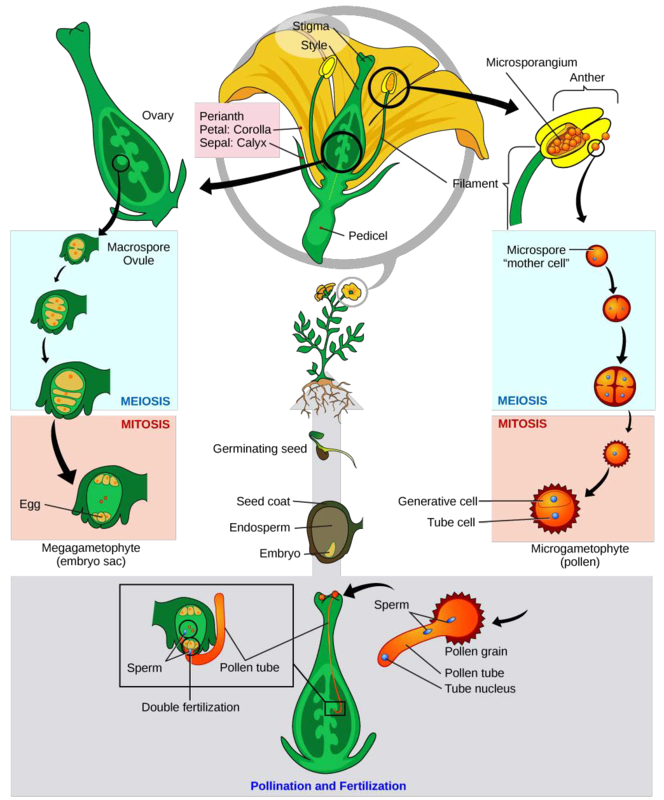
If a flower lacked a megasporangium, what type of gamete would it not be able to form? If it lacked a microsporangium, what type of gamete would not form?
In the ovules, the female gametophyte is produced when a megasporocyte undergoes meiosis to produce four haploid megaspores. One of these is larger than the others and undergoes mitosis to form the female gametophyte or embryo sac. Three mitotic divisions produce eight nuclei in seven cells. The egg and two cells move to one end of the embryo sac (gametophyte) and three cells move to the other end. Two of the nuclei remain in a single cell and fuse to form a 2nnucleus; this cell moves to the center of the embryo sac.
When a pollen grain reaches the stigma, a pollen tube extends from the grain, grows down the style, and enters through an opening in the integuments of the ovule. The two sperm cells are deposited in the embryo sac.
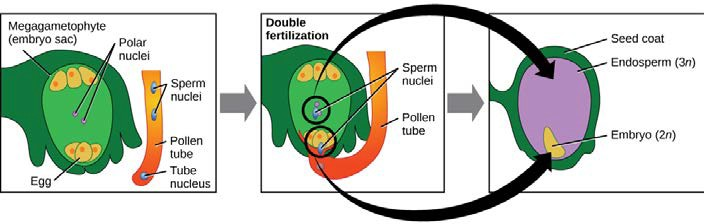
What occurs next is called a double fertilization event (Figure 14.27) and is unique to angiosperms. One sperm and the egg combine, forming a diploid zygote—the future embryo. The other sperm fuses with the diploid nucleus in the center of the embryo sac, forming a triploid cell that will develop into the endosperm: a tissue that serves as a food reserve. The zygote develops into an embryo with a radicle, or small root, and one or two leaf-like organs called cotyledons. Seed food reserves are stored outside the embryo, and the cotyledons serve as conduits to transmit the broken-down food reserves to the developing embryo. The seed consists of a toughened layer of integuments forming the coat, the endosperm with food reserves and, at the center, the well-protected embryo.
Most flowers carry both stamens and carpels; however, a few species self-pollinate. These are known as “perfect” flowers because they contain both types of sex organs (Figure 14.25. Biochemical and anatomical barriers to self-pollination promote cross-pollination. Self-pollination is a severe form of inbreeding, and can increase the number of genetic defects in offspring.
A plant may have perfect flowers, and thus have both genders in each flower; or, it may have imperfect flowers of both kinds on one plant (Figure 14.28). In each case, such species are called monoecious plants, meaning “one house.” Some botanists refer to plants with perfect flowers simply as hermaphroditic. Some plants are dioecious, meaning “two houses,” and have male and female flowers (“imperfect flowers”) on different plants. In these species, cross-pollination occurs all the time.

- 42458 reads






