Later in this chapter we will discuss some of the other types of reports you will want to be able to produce in order to plan and control your business finances, but for now, let us concentrate on the two most fundamental statements of all: The Income Statement and the Balance Sheet. The Income Statement is important because it will tell you if your business was profitable or not for any given period of time. The Balance Sheet will show you the financial condition of your business, what you own, what you owe, and the owners’ financial interest. You will sometimes hear the Income Statement referred to as the Profit and Loss Statement and the Balance Sheet called the Statement of Financial Condition.
Here’s a simple example of an Income Statement:
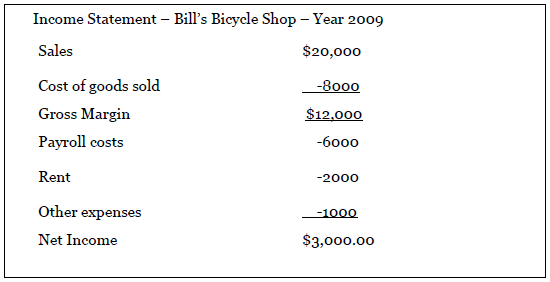
The only items that need additional explanation are “Cost of goods sold” and “gross margin”. The cost of goods sold is the total cost the owner of a business paid for products sold. If the owner of Bill’s Bicycle Shop simply buys bicycles from the manufacturer and has them shipped to the shop, the cost of a bicycle is whatever bill paid the manufacturer plus the cost of shipping it to the shop and any labor cost that might be involved in assembling the bicycle before putting it on display for customers to see. The Cost of goods sold shown on the Income Statement (USD 8,000) is the total costs associated with all of the bicycles sold by Bill in the year 2009. This is the accounting concept of “matching”. (The Sales figure of USD 20,000 is the total of the prices paid by all of the customers who bought bicycles from Bill during the year).
Gross margin is simply the difference between Sales and the Cost of goods sold. It is an important figure for owners to watch, and you will sometimes hear business owners talk about their margins or “managing their margins”. The greater the gross margin is the more profitable a business is likely to be. For example, see if you can determine what Bill’s gross margin and profit would be if he had to sell his bicycles at a discount because of competitive pressure and his sales revenue for the year amounted to USD 17,000 instead of USD 20,000.
This is, of course, a relatively simple example to illustrate the general outline of an Income Statement, but it should give you an appreciation of why the Income Statement is important to the owner of any business. Am I making money or not? And if not, why not?
Here’s a simple example of a Balance Sheet:
|
Assets |
|
|
Cash on hand and in bank |
USD 8,000 |
|
Accounts Receivable |
3000 |
|
Inventory – New Bicycles |
12000 |
|
Parts Inventory |
4000 |
|
Office Equipment |
2000 |
|
Repair Equipment |
1000 |
|
Total Assets |
USD 30,000 |
|
Liabilities |
|
|
Accounts Payable |
USD 10,000 |
|
Loan from Bank |
15,000 |
|
Total Liabilities |
25000 |
|
Owner’s Equity |
5000 |
|
Total Liabilities and Owner’s Equity |
USD 30,000 |
You can see why it is called a Balance Sheet. It is because the sum of the asset accounts must equal the sum of the liability and owner’s equity accounts. In other words, they must be in balance. You can also see why it is sometimes called a statement of financial position. It shows the condition of the business, in financial terms, as of a specific date.
Next, we will discuss a short history of accounting and the invention of double-entry bookkeeping, a technique that is of great assistance to accountants and bookkeepers in assuring the accuracy of accounting records and the reports that are prepared from them.
- 3582 reads






