We start by defining what we mean by growth and growth-oriented firms. Criteria such as growth in the number of employees, or sales growth are generally used by researchers. The Kaufmann Center for Entrepreneurial Leadership, a leading institute of entrepreneurial research in the USA, for example, defines high-growth firms as being those with over 30 per cent growth in sales or over 20 per cent growth in the number of employees for each of the three preceding years. Other US researchers (Siegel/MacMillan 1993) define strong growth as over 25 per cent growth per annum over a three-year period.
The number of high-growth firms is no doubt limited. Even in the USA, only 5 per cent of firms each year are estimated to take on extra staff (cf. Sexton/Bowman-Upton 1991, p. 12). However, these fast-growing firms have a disproportionate significance for the increase in the number of jobs. In the USA, for example, it is estimated that only 12-15 per cent of all businesses are responsible for 100 per cent of the employment growth in the US economy (cf. Sexton/Bowman-Upton 1991, p. 10). Research studies in Germany have also shown that businesses with 50 to 250 employees recorded the greatest increase in employment (cf. Kühlhorn/Wissdorf 2001). International comparative data can be found in the Global Entrepreneurship Monitor (GEM). Based on a survey of all start-ups from 1999, the GEM presented the share of high-growth start-ups (see Figure 15.1). (cf. Sternberg 2000).
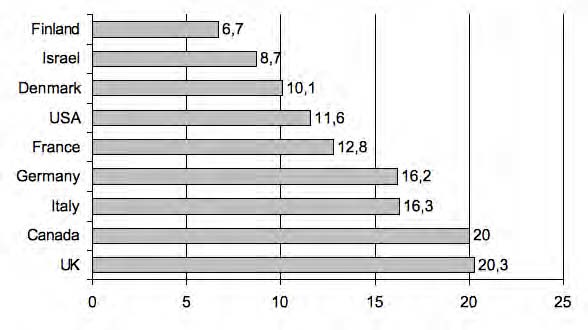
- 3878 reads






