As Figure 12.1 shows, the two-way interactions between a parent and its subsidiaries can take quite a complicated form, with various links in different currencies. The overall objective of the system is, of course, securing adequate funds for the operations of the MNC and all its subsidiaries. This objective is accomplished by synchronizing all policy tools available to each subsidiary and to the parent. Thus the MNC and its subsidiaries form a system of interrelated and interconnected units, each of which depends on the others for its operation and survival.
Within this system the task of the international financial manager can be visualized as depicted in Figure 12.2. Four interrelated functions constitute the heart of international financial management:
Function A: Exposure management-protecting the company's assets
Function B: Cash management-maneuvering liquid assets
Function C: Capital budgeting-evaluating fund uses (projects)
Function D: Funding-finding funds for projects
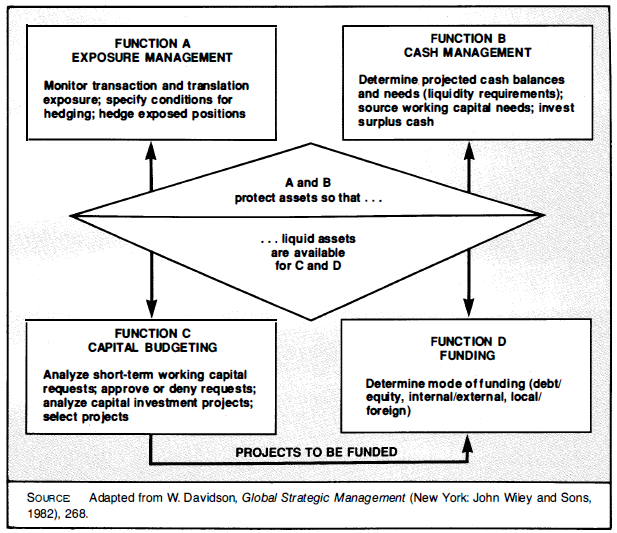
Financial managers estimate, record, and protect the firm's assets via external exposure management (function A) and internal cash management tools (function B). They also plan, propose, and evaluate projects (function C) which must be funded (function 0) to create the cash flows that must be managed to start the cycle again.
- 3651 reads






