The value added method of determining GNP is of particular interest to international business because a number of European countries use it for tax purposes. There is increasing talk of the United States' adopting this method of calculating GNP for taxation.
The value added by a firm is the revenues received from selling products, minus the amounts paid for goods and services purchased from other firms. According to the value added method of GNP estimation, the GNP is given by the sum of values added by all firms. Of course, what is added translates into the incomes received by the people and/or firms that participated in the process of successive additions of values. It follows, therefore, that
Value Added = Wages + Interest + Rents + Profits
so
GNP = Value Added = Wages + Interest + Rents + Profits
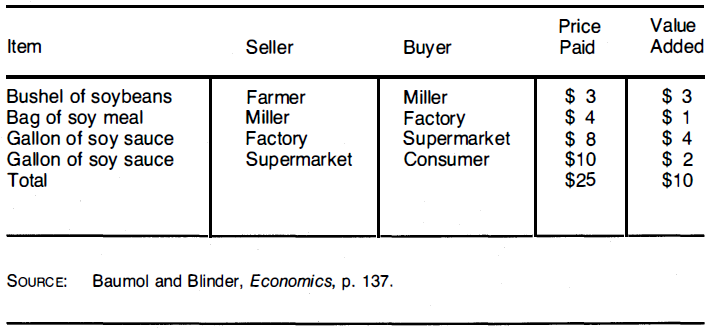
An example may help to illustrate the concept of value added. Suppose a farmer sells a bushel of soybeans for $3 to a miller, who grinds them and sells them for $4 to a factory, which makes soy sauce out of them and sells the soy sauce for $8 to a supermarket, which sells it to the consumer for $10. This product passes through three intermediate stages before it finally leaves the market by being consumed. In other words, in the course of the passage from the originator of the product (the farmer) to the end consumer (the customer), there are three points at which some value is added. These points are the miller's (value added = $1), the factory (value added = $4), and the supermarket (value added = $2). Add in the original value created by the farmer (value added = $3), to get the total value added of $10. The relationship between the price and the value added is illustrated in tabular form in Figure 6.2.
- 1955 reads






