Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Explain the process of DNA replication
- Explain the importance of telomerase to DNA replication
- Describe mechanisms of DNA repair
When a cell divides, it is important that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the DNA. This is accomplished by the process of DNA replication. The replication of DNA occurs during the synthesis phase, or S phase, of the cell cycle, before the cell enters mitosis or meiosis.
The elucidation of the structure of the double helix provided a hint as to how DNA is copied. Recall that adenine nucleotides pair with thymine nucleotides, and cytosine with guanine. This means that the two strands are complementary to each other. For example, a strand of DNA with a nucleotide sequence of AGTCATGA will have a complementary strand with the sequence TCAGTACT (Figure 9.8 ).
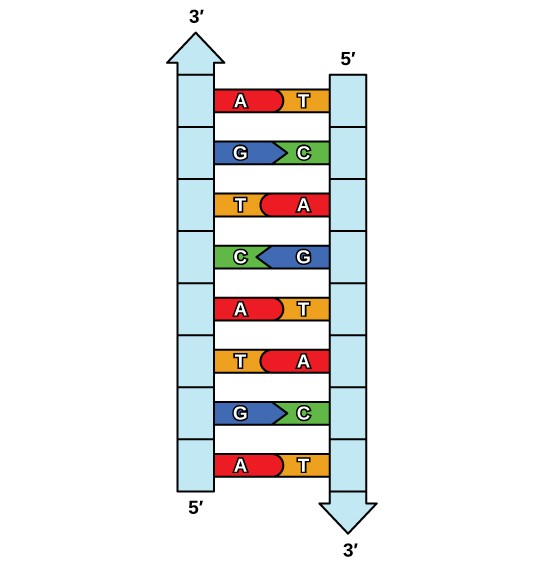
Because of the complementarity of the two strands, having one strand means that it is possible to recreate the other strand. This model for replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied (Figure 9.9).
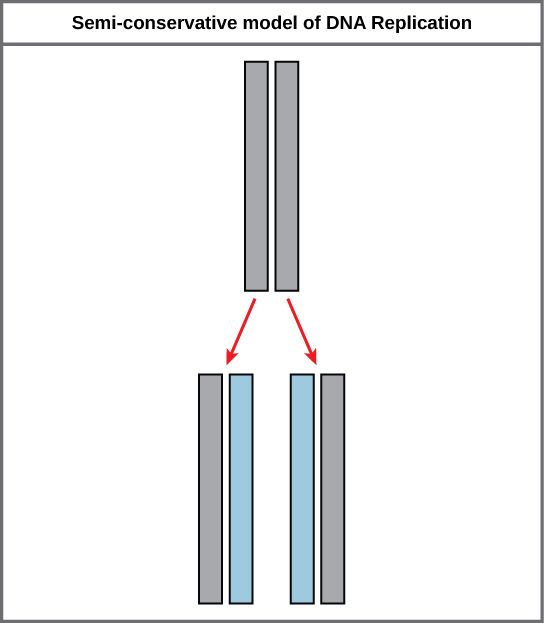
During DNA replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or “old” strand. Each new double strand consists of one parental strand and one new daughter strand. This is known as semiconservative replication. When two DNA copies are formed, they have an identical sequence of nucleotide bases and are divided equally into two daughter cells.
- 4815 reads






