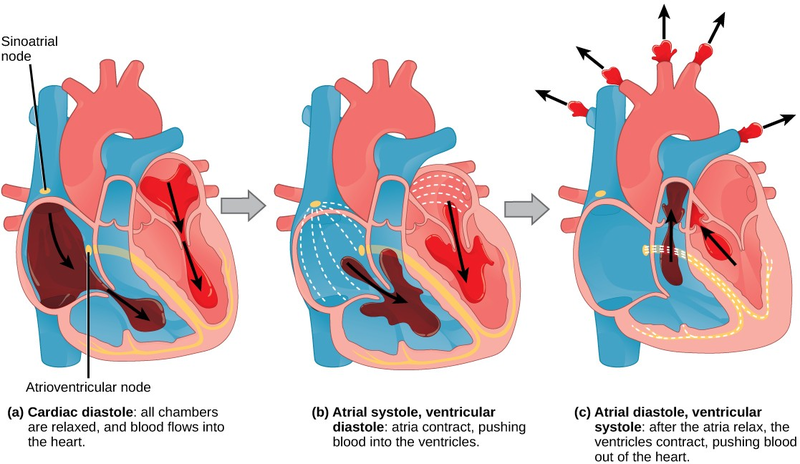
The main purpose of the heart is to pump blood through the body; it does so in a repeating sequence called the cardiac cycle. The cardiac cycle is the flow of blood through the heart coordinated by electrochemical signals that cause the heart muscle to contract and relax. In each cardiac cycle, a sequence of contractions pushes out the blood, pumping it through the body; this is followed by a relaxation phase, where the heart fills with blood. These two phases are called the systole (contraction) and diastole (relaxation), respectively (Figure 16.11). The signal for contraction begins at a location on the outside of the right atrium. The electrochemical signal moves from there across the atria causing them to contract. The contraction of the atria forces blood through the valves into the ventricles. Closing of these valves caused by the contraction of the ventricles produces a “lub” sound. The signal has, by this time, passed down the walls of the heart, through a point between the right atrium and right ventricle. The signal then causes the ventricles to contract. The ventricles contract together forcing blood into the aorta and the pulmonary arteries. Closing of the valves to these arteries caused by blood being drawn back toward the heart during ventricular relaxation produces a monosyllabic “dub” sound.
The pumping of the heart is a function of the cardiac muscle cells, or cardiomyocytes, that make up the heart muscle. Cardiomyocytes are distinctive muscle cells that are striated like skeletal muscle but pump rhythmically and involuntarily like smooth muscle; adjacent cells are connected by intercalated disks found only in cardiac muscle. These connections allow the electrical signal to travel directly to neighboring muscle cells.
The electrical impulses in the heart produce electrical currents that flow through the body and can be measured on the skin using electrodes. This information can be observed as an electrocardiogram (ECG) a recording of the electrical impulses of the cardiac muscle.
Visit the following website (http://openstaxcollege.org/l/electric_heart2) to see the heart’s pacemaker, or electrocardiogram system, in action.
- 3491 reads






