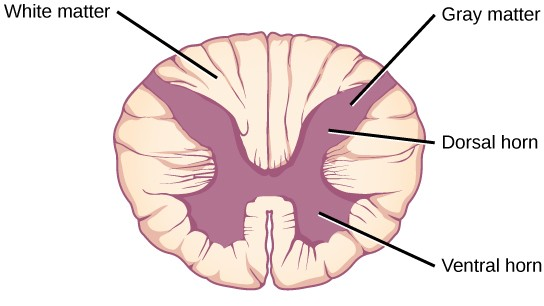
Connecting to the brainstem and extending down the body through the spinal column is the spinal cord. The spinal cord is a thick bundle of nerve tissue that carries information about the body to the brain and from the brain to the body. The spinal cord is contained within the meninges and the bones of the vertebral column but is able to communicate signals to and from the body through its connections with spinal nerves (part of the peripheral nervous system). A cross-section of the spinal cord looks like a white oval containing a gray butterfly-shape (Figure 16.23). Axons make up the “white matter” and neuron and glia cell bodies (and interneurons) make up the “gray matter.” Axons and cell bodies in the dorsa spinal cord convey mostly sensory information from the body to the brain. Axons and cell bodies in the spinal cord primarily transmit signals controlling movement from the brain to the body.
The spinal cord also controls motor reflexes. These reflexes are quick, unconscious movements—like automatically removing a hand from a hot object. Reflexes are so fast because they involve local synaptic connections. For example, the knee reflex that a doctor tests during a routine physical is controlled by a single synapse between a sensory neuron and a motor neuron. While a reflex may only require the involvement of one or two synapses, synapses with interneurons in the spinal column transmit information to the brain to convey what happened (the knee jerked, or the hand was hot).
- 3371 reads






