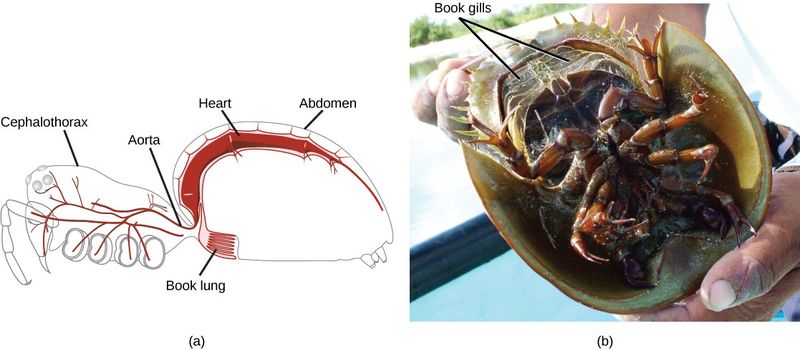
A unique feature of arthropods is the presence of a segmented body with fusion of certain sets of segments to give rise to functional segments. Fused segments may form a head, thorax, and abdomen, or a cephalothorax and abdomen, or a head and trunk. The coelom takes the form of a hemocoel(or blood cavity). The open circulatory system, in which blood bathes the internal organs rather than circulating in vessels, is regulated by a two-chambered heart. Respiratory systems vary, depending on the group of arthropod: Insects and myriapods use a series of tubes ( tracheae) that branch throughout the body, open to the outside through openings called spiracles, and perform gas exchange directly between the cells and air in the tracheae. Aquatic crustaceans use gills, arachnids employ “book lungs,” and aquatic chelicerates use “book gills.” The book lungs of arachnids are internal stacks of alternating air pockets and hemocoel tissue shaped like the pages of a book. The book gills of crustaceans are external structures similar to book lungs with stacks of leaf-like structures that exchange gases with the surrounding water (Figure 15.19).
- 5595 reads






