The flow of genetic information in cells from DNA to mRNA to protein is described by the central dogma (Figure 9.14), which states that genes specify the sequences of mRNAs, which in turn specify the sequences of proteins.
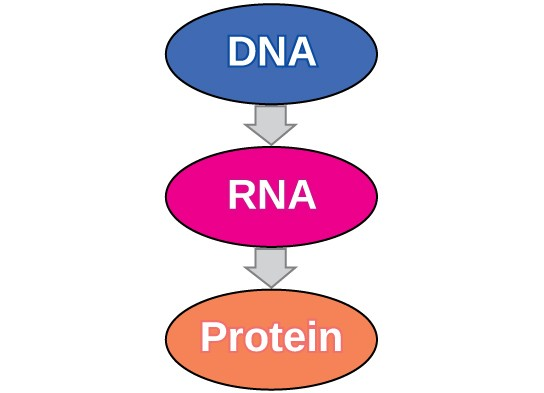
The copying of DNA to mRNA is relatively straightforward, with one nucleotide being added to the mRNA strand for every complementary nucleotide read in the DNA strand. The translation to protein is more complex because groups of three mRNA nucleotides correspond to one amino acid of the protein sequence. However, as we shall see in the next module, the translation to protein is still systematic, such that nucleotides 1 to 3 correspond to amino acid 1, nucleotides 4 to 6 correspond to amino acid 2, and so on.
- 3616 reads






