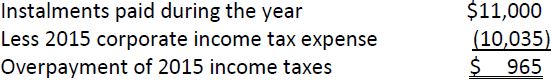|
1. |
Prepare necessary adjusting entries at December 31, 2015. Include general ledger account numbers and appropriate descriptions. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
a. |
2015 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dec. 31 |
Commissions Earned |
410 |
300 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Unearned Comm. Rev. |
242 |
300 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
To adjust unearned commissions revenue to actualat December 31. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
b. |
2015 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dec. 31 |
Parts Inventory |
151 |
1,000 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
GST Payable |
238 |
50 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Accounts Payable |
210 |
1,050 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
To record invoice from supplier. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
c. |
2015 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dec. 31 |
Accounts Receivable |
110 |
3,150 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Sales |
500 |
3,000 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
GST Payable |
238 |
150 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Cost of Goods Sold |
570 |
2,500 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Merchandize Inventory |
150 |
2,500 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
To record missing sales on account. (GST would have been paid when the inventory was originally purchased, so there is no GST effect related to cost of goods sold.) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
d. |
2015 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dec. 31 |
Interest Expense |
632 |
34 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Interest Payable |
222 |
34 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
To record interest on note payable [$10,000 x 4% x31/365 days = $34 (rounded)] |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
e. |
2015 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dec. 31 |
Estimated Warranty Liability |
213 |
600 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Cost of Goods Sold |
570 |
500 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Salaries Expense |
656 |
100 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
To reallocate warranty repair expenditures. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
f. |
2015 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dec. 31 |
Warranty Expense |
678 |
14,400 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Estimated Warranty Liab. |
213 |
14,400 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
To record estimated warranty expense for 2015[($477,000 + 3,0001) x 3% = $14,400] 1 See c. above |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
g. |
2015 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dec. 31 |
Salaries Expense |
656 |
5,000 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Gov’t Employment Ins. Exp. |
658 |
175 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Gov’t Pension Expense |
659 |
100 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Company Health Insur. Exp. |
660 |
75 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Company Pension Expense |
661 |
500 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Salaries Payable |
226 |
3,275 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Emp’ee Income Tax. Pay. |
227 |
1,000 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Employment Insur. Pay. |
228 |
300 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Gov’t Pension Payable |
229 |
200 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Co. Health Plan Payable |
230 |
125 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Union Dues Payable |
231 |
200 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Co. Pension Payable |
232 |
750 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
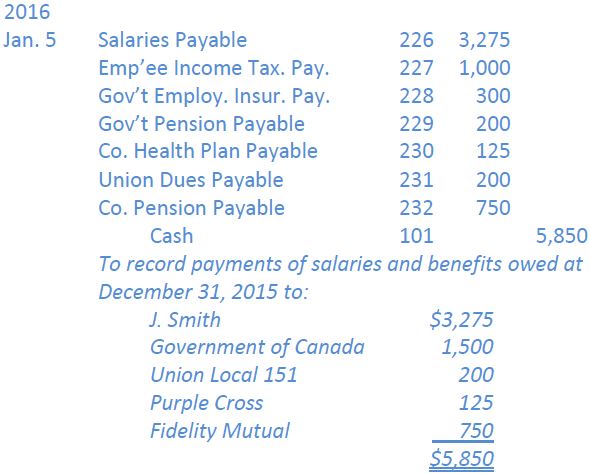
To record Dec. 24-31 salaries and benefits payableas follows: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
h. |
2015 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dec. 31 |
Professional Fees |
653 |
5,000 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Estimated Current Liab. |
212 |
5,000 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
To record estimated audit fees. (No GST will berecorded until the actual invoice is received.) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
i. |
No entry. This only affects balance sheet presentation between current and non-current liabilities. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
j. |
No entry. The event would only be recorded if the outcome was probable, even if the amount to be awarded can be reasonably estimated. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
k. |
2015 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dec. 31 |
Depreciation Expense – Bldg. |
621 |
8,940 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Accum. Dep’n – Bldg. |
191 |
8,940 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
To record depreciation expense for the year[(100%/10 yrs.) = 10% x 2 = 20%; ($214,700 –170,000) x 20% = $8,940]. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
l. |
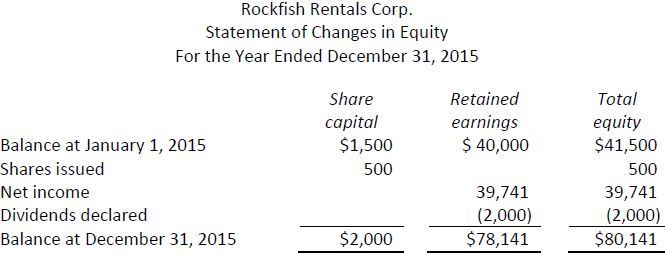
No entry. This should be shown on the statement of changes in equity, though. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
m. |
2015 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dec. 31 |
Corporate Income Taxes Exp. |
830 |
10,035 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Corporate Inc. Tax. Pay. |
260 |
10,035 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
To record corporate income taxes for the year[($50,1761 x 20% = $10,035 (rounded)] |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
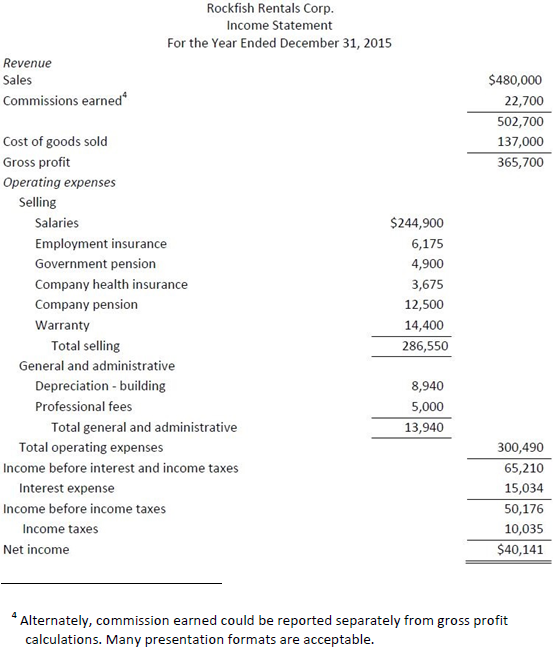
1 See income statement. This entry is recorded after the partial income statement is prepared up to the income before income taxes amount. The income statement can be completed after this entry is recorded. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
n. |
2015 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dec. 31 |
Dividends Declared |
350 |
2,000 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dividends Payable |
221 |
2,000 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
To record dividend declared, payable January 31,2016. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2. |
Post the entries to the “Adjustments” column of the worksheet. Total the worksheet. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
3. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
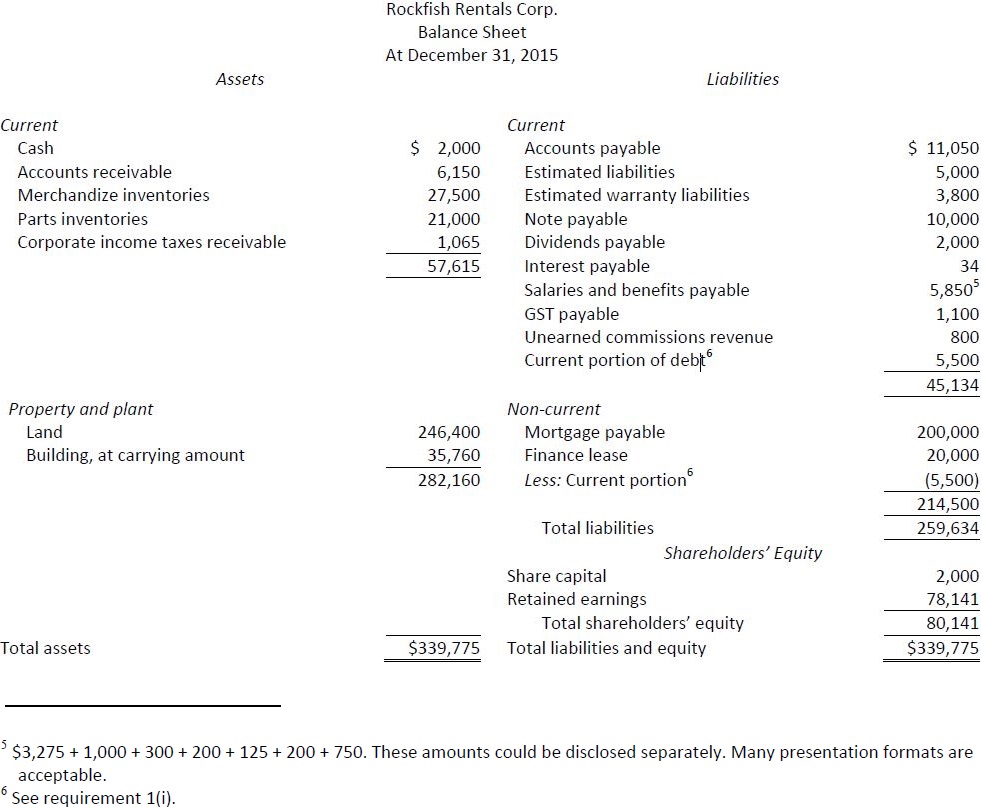
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
4. |
The journal entry to record payment of salaries and benefits payable would be: (Alternately, five separate entries could be made.) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
5. |
The journal entry to record the GST payment would be:
No payment would be made for corporate income taxes. There is an amount receivable of $965 from the government at December 31, 2015 represented by:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
6. |
The estimated warranty liability at December 31, 2014 was $30,000. It is only $3,800 at December 31, 2015. Management should review this. It may be that the estimated warranty expense of 3% of sales revenue is too low. Alternately, the amount of warranty claims in 2015 might have been abnormally high. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
7. |
A note should disclose more information about the note payable, the mortgage payable, and the finance lease – due dates, interest rates, repayment terms, and any assets pledged as security. A note should also disclose the details of the contingent liability related to the outstanding lawsuit. This should include the likelihood of success (possible) and the estimated amount of the award. Significant accounting policies should also be stated. These include depreciation rates and estimated useful lives of plant and equipment, and estimates used to establish some liabilities. The estimated warranty expense rate (3% of sales) should be disclosed, for instance. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- 3687 reads